North Korea: Position And Influence On The World Map
North Korea, officially known as the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country that has captured the world's attention for decades. Its geopolitical significance, coupled with its unique socio-political landscape, makes North Korea a country of great interest. As we delve into the topic of "North Korea in the World Map," we aim to explore its geographical placement, political influences, historical background, and its current role in global affairs. Understanding North Korea's position on the world map not only involves its geographical location but also its strategic importance and impact on international relations.
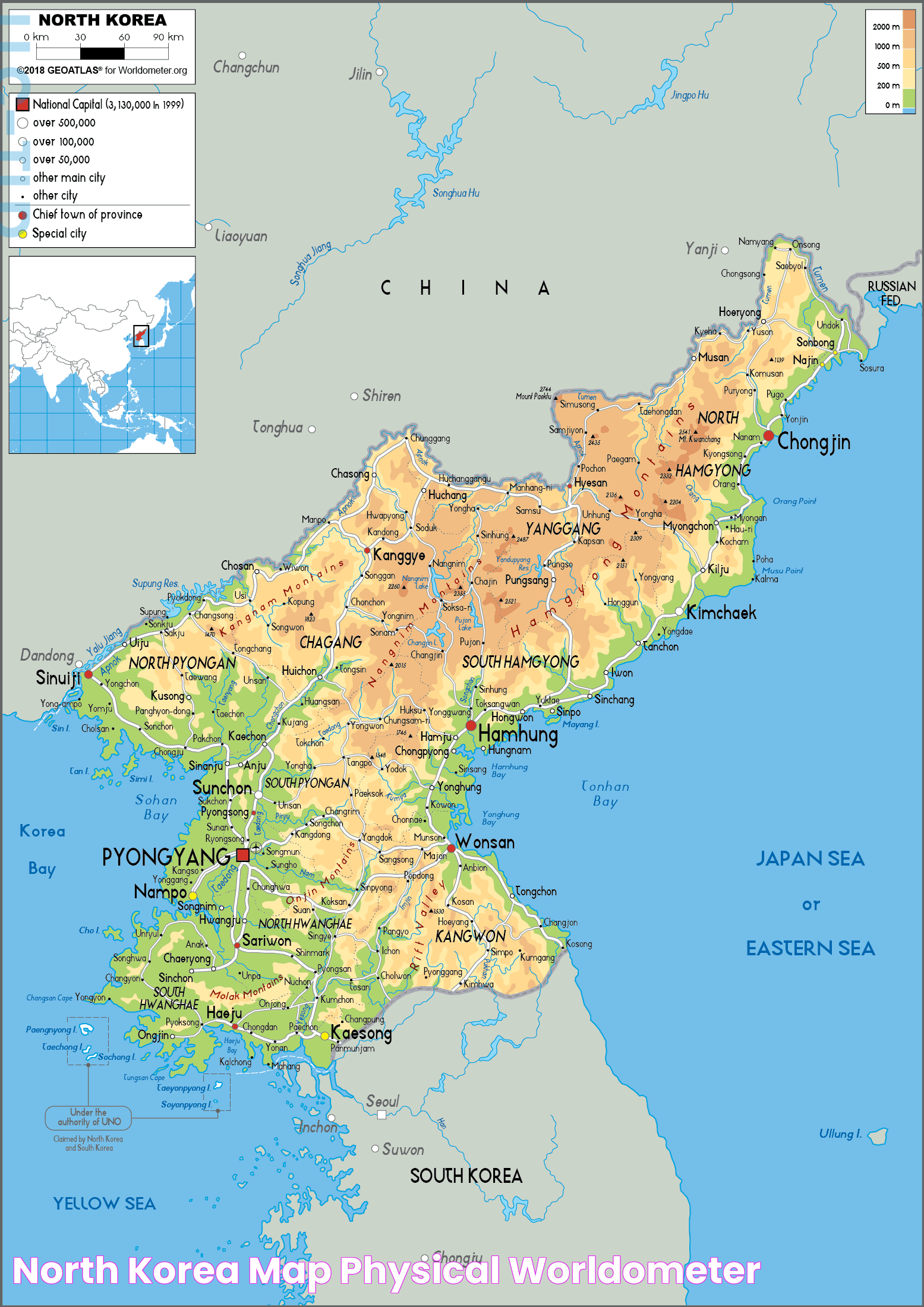
Situated in East Asia, North Korea occupies the northern half of the Korean Peninsula, bordered by China and Russia to the north, and South Korea to the south. The country's location plays a pivotal role in its interactions with neighboring countries and its stance in global politics. Despite its relatively small size, North Korea's influence in international matters is disproportionately significant, often making headlines for its nuclear ambitions, human rights issues, and economic challenges.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore various facets of North Korea's presence on the world map, including its historical evolution, cultural identity, economic dynamics, and military capabilities. We'll also delve into the country's relationship with major world powers, its participation in international organizations, and how these factors shape the global perception of North Korea. Through this exploration, we aim to provide a nuanced understanding of North Korea's place in the global arena, shedding light on the complexities and contradictions that define this enigmatic nation.
Read also:Innovative Screens The Role Of Tv In Modern Society
Table of Contents
- Historical Background of North Korea
- What is North Korea's Geographical Position?
- Understanding North Korea's Political Structure
- How Does North Korea's Economic Landscape Look?
- The Cultural Identity of North Korea
- Analyzing North Korea's Military Capabilities
- North Korea's Relationship with China
- North Korea's Relationship with Russia
- How Does North Korea Interact with South Korea?
- North Korea's Role in International Organizations
- What Are North Korea's Nuclear Ambitions?
- Examining Human Rights Issues in North Korea
- Global Perception of North Korea
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Historical Background of North Korea
To understand North Korea's current position on the world map, it's essential to delve into its historical background. The Korean Peninsula has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, with various kingdoms and dynasties shaping its cultural and political landscape. The division of Korea into North and South occurred after World War II, when the peninsula was liberated from Japanese occupation. The Soviet Union occupied the north while the United States occupied the south, leading to the establishment of two separate governments.
The Korean War (1950-1953) further solidified the division, with the North supported by China and the Soviet Union, and the South backed by the United Nations, primarily the United States. The war ended with an armistice agreement, but no formal peace treaty, leaving the two Koreas technically still at war. The Democratic People's Republic of Korea was established in 1948, with Kim Il-sung as its founding leader. His legacy and ideology, known as Juche, continue to influence North Korea's political and social systems.
North Korea's historical evolution has been marked by periods of isolation and engagement, as it navigates its interactions with the rest of the world. Its history is characterized by a strong emphasis on self-reliance, state control, and a centralized leadership structure. Understanding this background provides context for North Korea's current policies and its place on the world map.
What is North Korea's Geographical Position?
Geographically, North Korea is located in the northern part of the Korean Peninsula, covering an area of approximately 120,540 square kilometers. It shares borders with China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and South Korea to the south, with the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) serving as a buffer zone between the two Koreas. The country's eastern coastline is along the Sea of Japan (East Sea), while the western coast faces the Yellow Sea.
This strategic location places North Korea at the crossroads of major regional powers, making it a significant player in East Asian geopolitics. The country's mountainous terrain and proximity to the sea have historically influenced its economic activities, defense strategies, and cultural exchanges. The Yalu and Tumen rivers form natural boundaries with China and Russia, respectively, facilitating trade and diplomatic interactions.
North Korea's geographical position has also played a role in its military strategies, as its location necessitates a robust defense posture to counter perceived threats from neighboring countries and beyond. The country's proximity to key shipping lanes and trade routes further underscores its importance in regional security dynamics.
Read also:Nicola Coughlan Weight Loss Secrets And Strategies Revealed
Understanding North Korea's Political Structure
North Korea's political structure is characterized by its unique system of governance, which is based on the principles of Juche, or self-reliance. The country is a one-party state, led by the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK), with the Kim family dynasty at the helm. The supreme leader holds ultimate authority, with Kim Jong-un currently serving as the head of state.
The political system is highly centralized, with power concentrated in the hands of the ruling party and its leadership. The Supreme People's Assembly (SPA) is the country's legislative body, but its role is largely ceremonial, as real power resides with the ruling party and its committees. The National Defense Commission (NDC) and the Central Military Commission (CMC) are key institutions that oversee the country's military and defense policies.
North Korea's political structure is often described as a totalitarian regime, with strict control over public life, media, and dissent. The country's leadership employs a combination of propaganda, surveillance, and repression to maintain its grip on power. Despite these challenges, the regime has demonstrated resilience and adaptability, navigating internal and external pressures to remain a formidable presence on the world map.
How Does North Korea's Economic Landscape Look?
North Korea's economy is characterized by central planning, state ownership, and limited market reforms. The country operates under a socialist economic model, with the government controlling key industries, resources, and production. Agriculture, mining, and manufacturing are the main sectors of the economy, with limited engagement in international trade due to sanctions and isolationist policies.
The country's economic challenges are compounded by its political isolation, reliance on military spending, and limited access to foreign investment and technology. Despite these constraints, North Korea has made efforts to modernize its infrastructure and develop special economic zones to attract foreign investment, primarily from China and other sympathetic countries.
North Korea's economic landscape is also shaped by its reliance on informal markets, known as jangmadang, which have emerged as alternative sources of goods and services. These markets provide a glimpse into the resilience and adaptability of the North Korean people, who navigate the challenges of living under a centrally planned economy.
The Cultural Identity of North Korea
North Korea's cultural identity is deeply rooted in its history, traditions, and political ideology. The country's cultural policies are designed to promote national unity, loyalty to the leadership, and adherence to the principles of Juche. The government exerts significant influence over cultural expressions, with state-approved art, music, and literature serving as tools of propaganda and social control.
Despite these restrictions, North Korea has a rich cultural heritage, with traditional Korean customs and practices playing an integral role in daily life. Festivals, ceremonies, and cultural performances reflect the country's unique blend of historical influences and contemporary political themes. The Arirang Mass Games, for example, are a showcase of synchronized gymnastics, music, and dance that celebrate the achievements of the regime.
North Korea's cultural identity is also shaped by its education system, which emphasizes loyalty to the state and the leadership. The country's cultural policies aim to foster a sense of national pride and resilience, even as they limit exposure to outside influences and ideas.
Analyzing North Korea's Military Capabilities
North Korea is one of the most militarized nations in the world, with a significant portion of its resources devoted to defense and military development. The Korean People's Army (KPA) is the country's primary military force, comprising ground, naval, and air units. The KPA is supported by a vast network of paramilitary organizations, reserve forces, and civil defense units.
The country's military capabilities are a source of both regional and global concern, particularly its nuclear weapons program and missile development. North Korea has conducted multiple nuclear tests and missile launches, drawing condemnation and sanctions from the international community. The regime's pursuit of nuclear deterrence is seen as a means of securing its survival and asserting its sovereignty on the world stage.
North Korea's military strategy is shaped by its emphasis on asymmetric warfare, leveraging its nuclear and missile capabilities to counterbalance conventional military disadvantages. The country's military posture is also influenced by its historical experiences, geographic location, and perceived threats from neighboring countries and global powers.
North Korea's Relationship with China
China is North Korea's closest ally and largest trading partner, providing critical economic support and diplomatic backing to the regime. The relationship between the two countries is rooted in historical ties, shared ideological foundations, and mutual strategic interests. China played a key role in supporting North Korea during the Korean War and continues to be a vital source of economic aid and political support.
Despite this close relationship, there are tensions and complexities in the Sino-North Korean alliance. China's support for international sanctions on North Korea's nuclear program and its push for denuclearization have strained relations at times. However, China remains committed to maintaining stability on the Korean Peninsula and preventing regime collapse, which could result in regional instability and a potential influx of refugees.
North Korea's relationship with China is characterized by a delicate balance of cooperation and tension, as both countries navigate their respective interests and priorities. This relationship plays a crucial role in shaping North Korea's position on the world map and its interactions with other global powers.
North Korea's Relationship with Russia
Russia shares a small border with North Korea and has historically been an important ally and partner. The relationship between the two countries dates back to the Soviet era, with Russia providing economic, military, and diplomatic support to North Korea. In recent years, Russia has sought to strengthen its ties with North Korea, seeing it as a strategic partner in the region.
Russia's engagement with North Korea is driven by its desire to maintain influence in East Asia, counterbalance U.S. and Chinese dominance, and promote regional stability. The two countries have cooperated on various economic projects, including energy development and transportation infrastructure. Russia has also advocated for a diplomatic resolution to the North Korean nuclear issue, calling for dialogue and negotiations.
North Korea's relationship with Russia adds another layer to its geopolitical dynamics, providing an alternative source of support and partnership. This relationship is an essential component of North Korea's strategy to diversify its international alliances and enhance its position on the world map.
How Does North Korea Interact with South Korea?
The relationship between North and South Korea is complex and multifaceted, characterized by periods of tension and rapprochement. The two Koreas remain technically at war, with the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) serving as a heavily fortified buffer zone. Despite this, there have been numerous efforts to improve relations, with varying degrees of success.
Inter-Korean relations are influenced by a range of factors, including political leadership, regional dynamics, and global developments. Initiatives such as family reunions, cultural exchanges, and economic cooperation have been pursued to promote reconciliation and reduce tensions. However, issues related to denuclearization, military provocations, and human rights continue to pose significant challenges.
North Korea's interaction with South Korea is shaped by its strategic priorities, including the desire for security guarantees, economic development, and international recognition. The relationship between the two Koreas remains a critical factor in shaping regional stability and North Korea's position on the world map.
North Korea's Role in International Organizations
North Korea's participation in international organizations is limited, reflecting its isolationist policies and strained relations with the global community. The country is a member of the United Nations (UN) and various specialized agencies, but its engagement is often marked by contentious issues and confrontations.
The UN has imposed multiple sanctions on North Korea in response to its nuclear and missile activities, leading to diplomatic tensions and limited cooperation. Despite this, North Korea has sought to engage with international organizations on issues such as humanitarian aid, disaster relief, and cultural exchanges.
North Korea's role in international organizations is shaped by its desire to assert its sovereignty, seek legitimacy, and pursue its national interests. The country's interactions with these organizations are often influenced by its broader diplomatic strategies and geopolitical considerations.
What Are North Korea's Nuclear Ambitions?
North Korea's nuclear ambitions have been a focal point of international concern and diplomacy for decades. The regime views its nuclear program as a vital component of its national defense strategy, aimed at deterring external threats and ensuring regime survival. North Korea has conducted multiple nuclear tests and developed a range of ballistic missiles capable of reaching regional and global targets.
The pursuit of nuclear capabilities is driven by a combination of security, political, and strategic factors. North Korea seeks to leverage its nuclear program to gain international recognition, negotiate favorable terms in diplomatic engagements, and strengthen its bargaining position in regional security matters.
The international community, led by the United States and its allies, has sought to address North Korea's nuclear ambitions through a combination of sanctions, diplomatic negotiations, and security assurances. Efforts to denuclearize the Korean Peninsula have faced significant challenges, with North Korea demonstrating resilience and defiance in the face of external pressures.
Examining Human Rights Issues in North Korea
Human rights issues in North Korea are a significant concern for the international community, with numerous reports documenting widespread violations and abuses. The regime's authoritarian control, lack of political freedoms, and extensive surveillance apparatus contribute to a climate of fear and repression.
Human rights organizations and UN bodies have highlighted issues such as arbitrary detention, forced labor, restricted freedom of expression, and severe limitations on freedom of movement. The country's penal system, including political prison camps, is notorious for harsh conditions and abuses.
North Korea's human rights record is a contentious issue in international diplomacy, with calls for accountability and reform often met with resistance from the regime. Efforts to address these issues are complicated by the country's isolation, geopolitical considerations, and the prioritization of security concerns over human rights.
Global Perception of North Korea
The global perception of North Korea is shaped by a variety of factors, including its political ideology, military activities, and human rights record. The country is often portrayed as a secretive and repressive regime, with a focus on its nuclear ambitions and confrontational foreign policy.
Media coverage and public discourse often highlight the eccentricities of the regime, its isolationist policies, and the challenges faced by its citizens. These perceptions are influenced by geopolitical dynamics, historical narratives, and cultural representations.
Despite these perceptions, there are efforts to promote a more nuanced understanding of North Korea, recognizing its complex history, cultural identity, and strategic interests. Engaging with North Korea through dialogue, cultural exchanges, and humanitarian initiatives can help bridge the gap between perception and reality, fostering greater understanding and cooperation on the world stage.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the capital of North Korea?
The capital of North Korea is Pyongyang, which is also the largest city in the country and serves as its political, economic, and cultural center.
2. How does North Korea's government control information?
North Korea's government controls information through strict censorship, state-run media, and limited access to the internet. The regime employs propaganda to shape public perceptions and maintain control over the population.
3. What are the main economic activities in North Korea?
The main economic activities in North Korea include agriculture, mining, and manufacturing. The country also engages in limited trade with select partners, primarily China and Russia.
4. How does North Korea interact with the United Nations?
North Korea is a member of the United Nations, but its interactions are often marked by tensions and disagreements, particularly concerning its nuclear program and human rights record.
5. What is the significance of the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)?
The Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is a buffer zone between North and South Korea, established to reduce military tensions and prevent conflict. It is one of the most heavily fortified borders in the world.
6. How does North Korea's nuclear program impact global security?
North Korea's nuclear program poses a significant challenge to global security, raising concerns about regional stability, proliferation risks, and the potential for conflict. It has been a focal point of international diplomacy and efforts to promote denuclearization.
Conclusion
North Korea's position on the world map is a complex tapestry of history, geography, politics, and culture. Its strategic location and unique political system have made it a focal point of international attention and concern. As we continue to explore and understand the intricacies of this enigmatic nation, it is essential to approach the subject with a balanced perspective, recognizing both the challenges and opportunities that define North Korea's role in the global arena.
Through a comprehensive examination of North Korea's historical background, geographical position, political structure, economic landscape, and cultural identity, we gain valuable insights into its influence and interactions on the world map. By fostering dialogue, cooperation, and understanding, we can contribute to a more stable and peaceful future for the Korean Peninsula and the broader international community.
Article Recommendations

