Comprehending The Pheromones Definition: An Insightful Guide
Pheromones, a term often heard yet seldom understood, play a crucial role in the communication systems of various organisms. These chemical signals are pivotal in influencing social behaviors, mating rituals, and territorial boundaries among animals. Humans, too, are subject to the subtle influences of pheromones, which can affect moods and interpersonal interactions in profound ways. Despite their invisible nature, pheromones have a powerful impact on the way living beings interact with each other and their environment.
In the realm of biology, pheromones are often described as the silent language of creatures, providing a means of communication that transcends verbal and visual exchanges. The study of pheromones encompasses a wide range of scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biology, and psychology. By understanding pheromones, researchers can uncover the hidden mechanisms behind behavioral patterns and interactions in the animal kingdom as well as in human societies.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of pheromones, it becomes clear that these chemical signals are not only fascinating but also essential to the survival and evolution of species. They serve as a bridge between instinct and behavior, guiding organisms in their daily lives. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the pheromones definition, exploring their types, functions, and the scientific principles behind their operation, while also examining their applications and implications in modern society.
Read also:Guide To Shopping Smart At A Converse Outlet Tips Deals And More
Table of Contents
- What are Pheromones?
- Historical Background of Pheromones
- Types of Pheromones
- How Do Pheromones Work?
- Pheromones in Animals
- Pheromones in Humans: Fact or Fiction?
- Scientific Research on Pheromones
- Applications of Pheromones
- Pheromones in Agriculture
- Pheromones in Medicine
- Pheromones and Human Behavior
- Controversies Surrounding Pheromones
- Future of Pheromone Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What are Pheromones?
Pheromones are chemical substances produced and released into the environment by animals and humans, affecting the behavior and physiology of others of the same species. These chemical signals are a form of communication that can trigger various responses such as mating, aggression, or even marking territory. They play a significant role in the ecology and social interactions of organisms, serving as invisible messengers that convey crucial information.
Historical Background of Pheromones
The concept of pheromones dates back to the mid-20th century when scientists first identified these chemical signals in insects. The term "pheromone" was coined by Peter Karlson and Martin Lüscher in 1959, derived from the Greek words "pherein" (to transport) and "hormone" (to stimulate). Since then, the study of pheromones has expanded to include a wide range of species, revealing their importance in both animal and human interactions.
Types of Pheromones
Pheromones can be categorized into several types based on their function and the responses they elicit:
- Releaser Pheromones: These pheromones trigger an immediate behavioral response, such as attraction or aggression.
- Primer Pheromones: These influence long-term physiological changes, such as reproductive cycles.
- Signal Pheromones: These provide information about the sender, such as identity or reproductive status.
- Modulator Pheromones: These alter the emotional state of the receiver, affecting mood and perception.
How Do Pheromones Work?
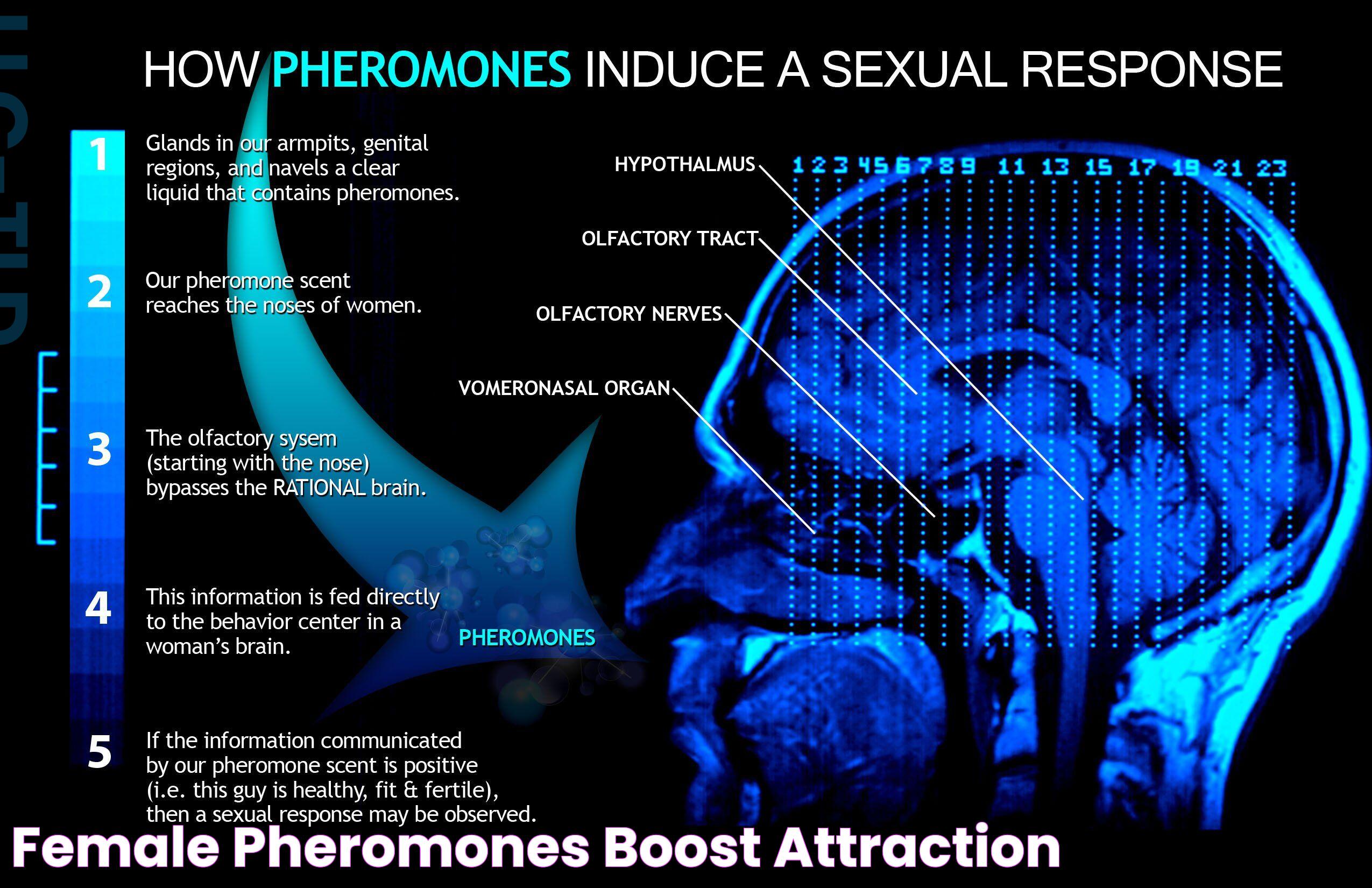
Pheromones work by binding to specific receptors in the olfactory system, which then transmit signals to the brain, eliciting a response. In animals, these chemical signals are detected by the vomeronasal organ (VNO), a specialized structure in the nasal cavity. In humans, the role of the VNO is still debated, but it is thought that pheromones might be detected through the main olfactory system.
Pheromones in Animals
In the animal kingdom, pheromones are crucial for survival and reproduction. They help animals find mates, establish dominance, and coordinate social behaviors. For instance, ants use trail pheromones to guide their colony to food sources, while mammals use pheromones to mark territory and signal reproductive readiness.
Pheromones in Humans: Fact or Fiction?
The existence and influence of pheromones in humans have been a topic of debate among scientists. While there is evidence that humans produce and respond to pheromones, the extent of their impact on behavior and physiology is still unclear. Some studies suggest that pheromones can influence attraction and mood, while others argue that their effects are minimal compared to other sensory inputs.
Read also:Taylor Swifts Sydney Extravaganza Experience The Magic Down Under
Scientific Research on Pheromones
Research on pheromones has advanced significantly over the years, with studies focusing on their chemical composition, mechanisms of action, and effects on behavior. Advances in technology have allowed scientists to isolate and identify specific pheromones, leading to a better understanding of their role in communication and interaction.
Applications of Pheromones
Pheromones have practical applications in various fields, including pest control, agriculture, and medicine. Synthetic pheromones are used to attract and trap pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. In medicine, pheromones are being studied for their potential in treating disorders related to mood and social behavior.
Pheromones in Agriculture
Pheromones are widely used in agriculture to manage pest populations and improve crop yields. By using pheromone traps, farmers can monitor and control pest infestations, reducing crop damage and the reliance on harmful pesticides. This environmentally friendly approach is becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable farming practice.
Pheromones in Medicine
The potential of pheromones in medicine is an emerging area of research. Scientists are exploring their use in developing treatments for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and social disorders. Pheromones might also play a role in enhancing the effectiveness of therapies for mood and behavioral issues.
Pheromones and Human Behavior
While the influence of pheromones on human behavior is not fully understood, there is evidence to suggest that they can affect mood, attraction, and social interactions. Studies have shown that certain pheromones can enhance perceived attractiveness and increase feelings of relaxation and well-being.
Controversies Surrounding Pheromones
The study of pheromones is not without controversy. Critics argue that the effects of pheromones are overstated and that other factors, such as personal preferences and social conditioning, play a more significant role in human behavior. Additionally, the commercial exploitation of pheromones in products such as perfumes and colognes has been met with skepticism.
Future of Pheromone Research
The future of pheromone research is promising, with potential breakthroughs in understanding their mechanisms and applications. As technology advances, researchers are likely to uncover more about the complex interactions between pheromones and behavior, paving the way for innovative solutions in fields such as health, agriculture, and environmental conservation.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are pheromones?
Pheromones are chemical substances released by organisms that influence the behavior or physiology of others of the same species. - Do humans produce pheromones?
Yes, humans produce pheromones, although their effects on behavior and physiology are still being studied. - Can pheromones affect human attraction?
Some studies suggest that pheromones can influence attraction, but the extent of their effect is still a topic of research. - Are pheromones used in pest control?
Yes, synthetic pheromones are used in pest control to attract and trap pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. - What is the role of pheromones in animals?
In animals, pheromones play a crucial role in communication, mating, and social interactions. - Is the use of pheromones in perfumes effective?
While pheromones are marketed in perfumes, their effectiveness in influencing attraction is debated and varies among individuals.
Conclusion
The study of pheromones offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of chemical communication and its impact on behavior and interaction. While much remains to be discovered, the knowledge gained so far underscores the significance of pheromones in both the animal kingdom and human societies. As research continues to advance, the potential for harnessing pheromones in various applications, from agriculture to medicine, holds promise for innovative and sustainable solutions.
Article Recommendations

