Exploring Treatments And Understanding The Impact Of HSDD Disorder On Life
Understanding HSDD disorder is crucial for both affected individuals and their partners, as it can significantly impact relationships and overall quality of life. The causes of HSDD are multifaceted, involving a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. These factors can include hormonal imbalances, psychological issues such as depression or anxiety, and societal pressures or relationship dynamics. Recognizing the complexity of HSDD is the first step toward seeking appropriate treatment and support. The journey to addressing HSDD disorder involves exploring various treatment options, ranging from medical interventions to therapy and lifestyle changes. It's essential to approach this condition with an open mind and a willingness to explore different strategies to find what works best for each individual. By raising awareness and promoting understanding, we can help those affected by HSDD to lead more fulfilling lives, free from the distress and limitations imposed by this disorder.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder |
| Common Abbreviation | HSDD |
| Primary Symptom | Lack of sexual desire |
| Prevalence | More common in women |
| Causes | Biological, psychological, and social factors |
| Treatment | Medical interventions, therapy, lifestyle changes |
Table of Contents
- What is HSDD Disorder?
- Symptoms of HSDD
- Causes Behind HSDD
- Diagnosing HSDD
- Treatment Options for HSDD
- Medications Used in HSDD Treatment
- Psychological Therapies for HSDD
- Impact of Lifestyle Changes
- How Does HSDD Affect Relationships?
- Can Men Experience HSDD?
- HSDD and Mental Health
- The Role of Hormones in HSDD
- HSDD Disorder in Different Age Groups
- Living with HSDD
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is HSDD Disorder?
Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD) is a condition characterized by a chronic lack of sexual desire that causes significant distress or interpersonal difficulties. It is more prevalent among women, though men can also be affected. The disorder is recognized by its persistent nature, differing from temporary decreases in libido that may occur due to stress or life changes.
HSDD is classified within the realm of sexual dysfunctions and is considered a medical condition when it leads to personal distress or strain in intimate relationships. The lack of sexual interest is not due to another medical condition, a mental health disorder, relationship issues, or the effects of substances such as drugs or medication.
Read also:Og Anunoby Stats A Complete Breakdown Of His Career And Achievements
Is HSDD Common?
HSDD is one of the most common sexual disorders reported by women. Studies suggest that up to one-third of women may experience low sexual desire at some point in their lives, but not all will meet the criteria for HSDD. It is essential to differentiate between a general low libido and HSDD, as the latter is marked by significant distress and impact on one's life.
How is HSDD Different from Other Sexual Disorders?
Unlike other sexual disorders that may focus on physical aspects of sexual function, such as arousal or orgasm, HSDD is primarily concerned with the psychological aspect of desire. It is also distinct from aversion disorders, where there is a repulsion to sexual activity, or arousal disorders, where the desire may be present but the body does not respond.
Symptoms of HSDD
The primary symptom of HSDD is a consistent lack of sexual desire. However, this lack of desire must cause marked distress or difficulties in relationships to be classified as HSDD. Other symptoms may include:
- A lack of interest in sexual activity
- Few or no erotic thoughts or fantasies
- Disinterest in initiating sex
- Reduced enjoyment of sexual activities
Can Symptoms Vary Among Individuals?
Yes, symptoms can vary significantly among individuals. Some may experience a total lack of interest in sex, while others may have some desire but not at a level they or their partners find satisfactory. The degree of distress caused by these symptoms also varies, influencing the impact of the disorder on personal and relational well-being.
What Are the Emotional Impacts of HSDD?
The emotional impact of HSDD can be profound. Individuals may experience feelings of inadequacy, frustration, or guilt. These emotions can further exacerbate the condition, creating a cycle of decreased desire and increased distress. Recognizing and addressing these emotional responses is a crucial part of managing HSDD.
Causes Behind HSDD
The causes of HSDD are complex and multifactorial, often involving an interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors. Understanding these causes can help in developing a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual's needs.
Read also:Jlo Drama The Intriguing World Of Jennifer Lopezs Life
Biological Factors
Biological factors may include hormonal imbalances, such as low levels of estrogen or testosterone, which can affect sexual desire. Other medical conditions or medications can also contribute to the development of HSDD.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors play a significant role in HSDD. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, or stress can diminish sexual interest. Past experiences, such as trauma or abuse, may also impact desire.
Social and Relationship Factors
Social norms and relationship dynamics can influence sexual desire. Issues such as communication problems, lack of intimacy, or conflicts within a relationship can contribute to HSDD. Cultural attitudes towards sex and gender roles may also play a part.
Diagnosing HSDD
Diagnosing HSDD involves a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional. This assessment typically includes discussions about sexual history, emotional well-being, and any potential contributing factors. The goal is to identify the specific aspects of the individual's experience that may be contributing to the disorder.
What Tests are Conducted?
While there are no specific tests to diagnose HSDD, healthcare providers may conduct blood tests to check hormone levels or screen for other medical conditions that could be affecting sexual desire. Psychological assessments may also be used to evaluate mental health conditions that could contribute to symptoms.
How is a Diagnosis Confirmed?
A diagnosis of HSDD is confirmed when a lack of sexual desire causes significant distress or relationship difficulties and is not better explained by another medical condition, mental health disorder, or substance use. The healthcare provider will consider all aspects of the individual's health and lifestyle before making a diagnosis.
Treatment Options for HSDD
Treating HSDD involves a combination of approaches tailored to the individual's specific needs. These can include medical treatments, therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Medical Interventions
Medical treatments may involve hormone therapy or medications designed to enhance sexual desire. These treatments can be effective for individuals whose HSDD has a biological basis.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common psychological approach used to address HSDD. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to sexuality and desire.
Sex Therapy
Sex therapy focuses on improving communication and intimacy between partners. It can be beneficial for those whose HSDD is related to relationship issues.
Medications Used in HSDD Treatment
Several medications have been approved for the treatment of HSDD, particularly in women. These medications aim to address hormonal imbalances or enhance sexual desire through other mechanisms.
Flibanserin
Flibanserin is a medication specifically approved for premenopausal women with HSDD. It works by balancing neurotransmitters in the brain to improve sexual desire.
Bremelanotide
Bremelanotide is another medication used to treat HSDD in women. It is administered as a subcutaneous injection and works by activating pathways in the brain associated with sexual desire.
Psychological Therapies for HSDD
Psychological therapies can be an effective part of treatment for HSDD, especially when psychological or relational factors are involved. These therapies focus on addressing underlying issues and improving sexual function.
Mindfulness-Based Therapy
Mindfulness-based therapy involves teaching individuals to focus on the present moment and reduce stress and anxiety related to sexual activity. This approach can help enhance sexual desire and satisfaction.
Counseling and Psychotherapy
Counseling and psychotherapy can help individuals explore emotional and psychological factors contributing to HSDD. Therapy can be conducted individually or with a partner to address relationship dynamics.
Impact of Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing HSDD. These changes can help improve overall health and well-being, which can, in turn, enhance sexual desire.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can improve mood, reduce stress, and boost energy levels, all of which can positively impact sexual desire. Exercise also promotes better body image, which can enhance confidence and interest in sexual activities.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support hormonal balance and overall health. Certain foods, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids or antioxidants, may also promote sexual health.
How Does HSDD Affect Relationships?
HSDD can have a significant impact on relationships, often leading to misunderstandings, frustration, and a lack of intimacy between partners. Communication is key to navigating these challenges and finding solutions that work for both individuals.
What Role Does Communication Play?
Open and honest communication is crucial in relationships affected by HSDD. Partners should feel comfortable discussing their feelings, concerns, and desires without fear of judgment or rejection. This dialogue can help identify underlying issues and foster a supportive environment for addressing the disorder.
How Can Partners Support Each Other?
Partners can support each other by being patient, understanding, and willing to explore treatment options together. It's essential to approach the situation as a team, seeking solutions that benefit both individuals and strengthen the relationship.
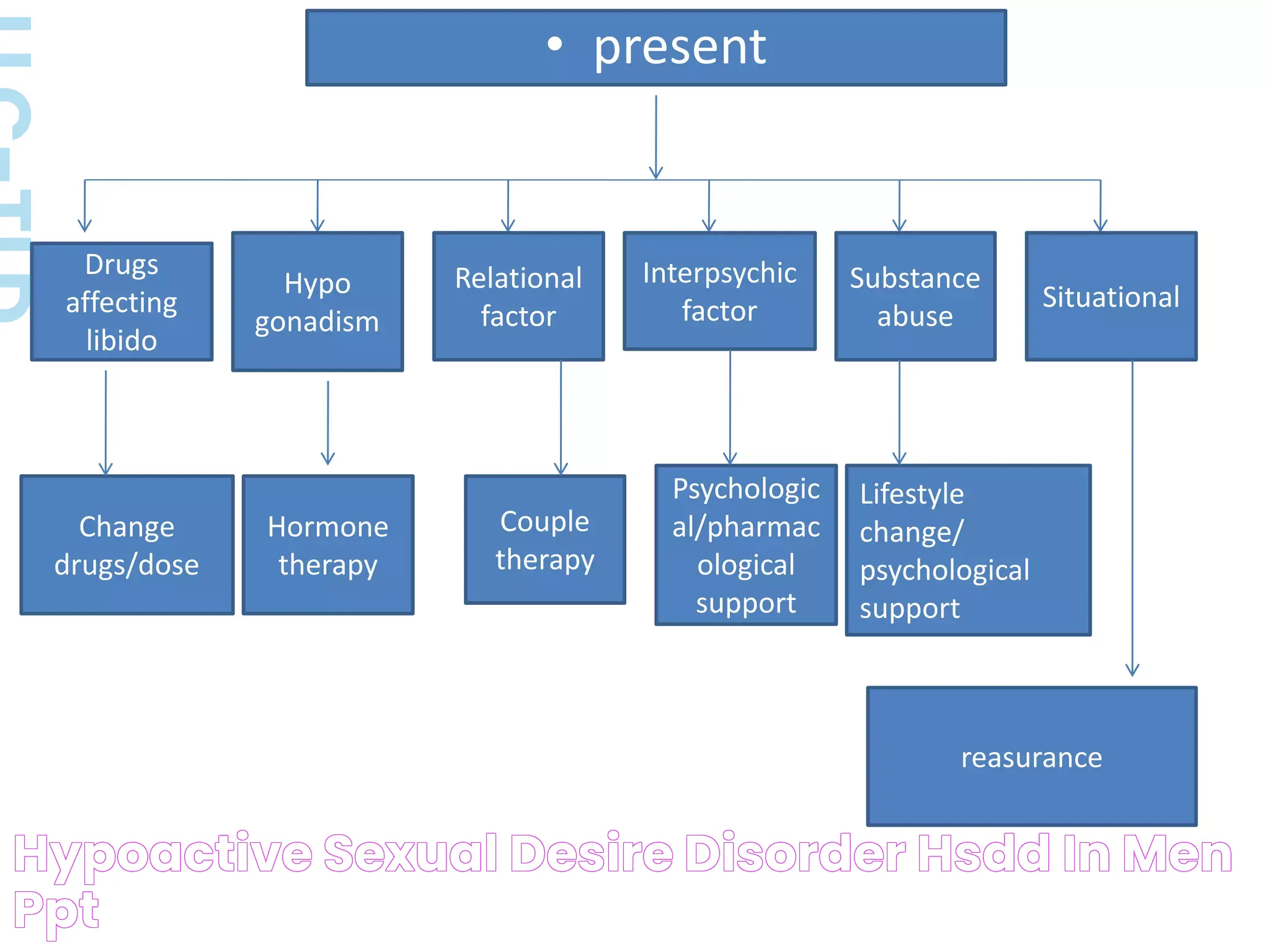
Can Men Experience HSDD?
While HSDD is more commonly associated with women, men can also experience this disorder. The symptoms and underlying causes may differ, but the impact on relationships and personal well-being can be just as significant.
What Are the Symptoms in Men?
In men, HSDD may manifest as a lack of interest in sexual activity, reduced enjoyment of sexual experiences, or a decrease in spontaneous sexual thoughts. As with women, these symptoms must cause significant distress or relationship issues to be classified as HSDD.
How is HSDD in Men Treated?
Treatment for men with HSDD may involve addressing underlying medical or psychological issues, such as hormonal imbalances or mental health disorders. Therapy and lifestyle changes can also be effective components of a comprehensive treatment plan.
HSDD and Mental Health
Mental health plays a crucial role in HSDD, as psychological factors often contribute to the condition. Addressing mental health concerns can be a vital part of effective treatment.
What is the Connection Between HSDD and Mental Health?
Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or stress can significantly impact sexual desire. These conditions may alter brain chemistry or lead to negative thought patterns that diminish interest in sexual activity.
How Can Mental Health be Addressed in HSDD Treatment?
Addressing mental health in HSDD treatment may involve therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Therapies such as CBT or mindfulness-based approaches can help individuals manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
The Role of Hormones in HSDD
Hormones play a significant role in regulating sexual desire, and imbalances can contribute to HSDD. Understanding these hormonal influences can inform treatment strategies.
Which Hormones Affect Sexual Desire?
Key hormones that affect sexual desire include estrogen, testosterone, and progesterone. Imbalances in these hormones can lead to decreased libido and HSDD.
How are Hormonal Imbalances Treated?
Treatment for hormonal imbalances may involve hormone replacement therapy or medications that address specific hormonal deficiencies. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate treatment based on individual needs and medical history.
HSDD Disorder in Different Age Groups
HSDD can affect individuals at various stages of life, with different challenges and considerations for each age group.
How Does HSDD Affect Younger Individuals?
In younger individuals, HSDD may be influenced by factors such as stress, body image concerns, or relationship dynamics. Addressing these issues through therapy or lifestyle changes can be beneficial.
What About Older Adults?
In older adults, HSDD may be related to hormonal changes, medical conditions, or medications. Treatment for this age group may focus on addressing these underlying factors and promoting overall health and well-being.
Living with HSDD
Living with HSDD can be challenging, but with the right support and treatment, individuals can manage the disorder and lead fulfilling lives.
What Strategies Can Help?
Strategies for living with HSDD include seeking professional help, maintaining open communication with partners, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits. Support groups or counseling can also provide valuable resources and encouragement.
How Can Individuals Maintain a Positive Outlook?
Maintaining a positive outlook involves recognizing that HSDD is a manageable condition and seeking solutions that work for the individual. Focusing on personal strengths and building a supportive network can help individuals navigate the challenges of HSDD.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between HSDD and low libido?
While both involve a lack of sexual desire, HSDD is characterized by significant distress and impact on one's life, whereas low libido may not necessarily cause distress or relationship issues.
Can lifestyle changes alone treat HSDD?
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing HSDD, but comprehensive treatment often involves a combination of approaches, including medical interventions and therapy.
Is HSDD a permanent condition?
HSDD is not necessarily permanent. With appropriate treatment and support, many individuals can successfully manage the disorder and experience improvements in sexual desire.
How can partners support someone with HSDD?
Partners can support someone with HSDD by being patient, understanding, and willing to communicate openly about feelings and concerns. Seeking treatment together can also strengthen the relationship.
Are there any natural remedies for HSDD?
Some individuals find that natural remedies, such as herbal supplements or lifestyle changes, can help manage HSDD. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new remedies.
Can HSDD affect men and women equally?
HSDD is more commonly diagnosed in women, but men can also experience the disorder. The symptoms and causes may differ, but the impact on relationships and personal well-being can be similar.
Conclusion
HSDD disorder is a complex condition that affects many individuals, primarily women, and can significantly impact personal well-being and relationships. Understanding the multifaceted nature of HSDD is crucial for seeking effective treatment and support. By exploring a combination of medical interventions, therapy, and lifestyle changes, individuals can manage the disorder and lead fulfilling lives. Open communication, patience, and a willingness to explore different strategies are key to navigating the challenges of HSDD and fostering stronger, more supportive relationships.
Article Recommendations

