Traumatic Disorder: Navigating Challenges And Pathways To Recovery
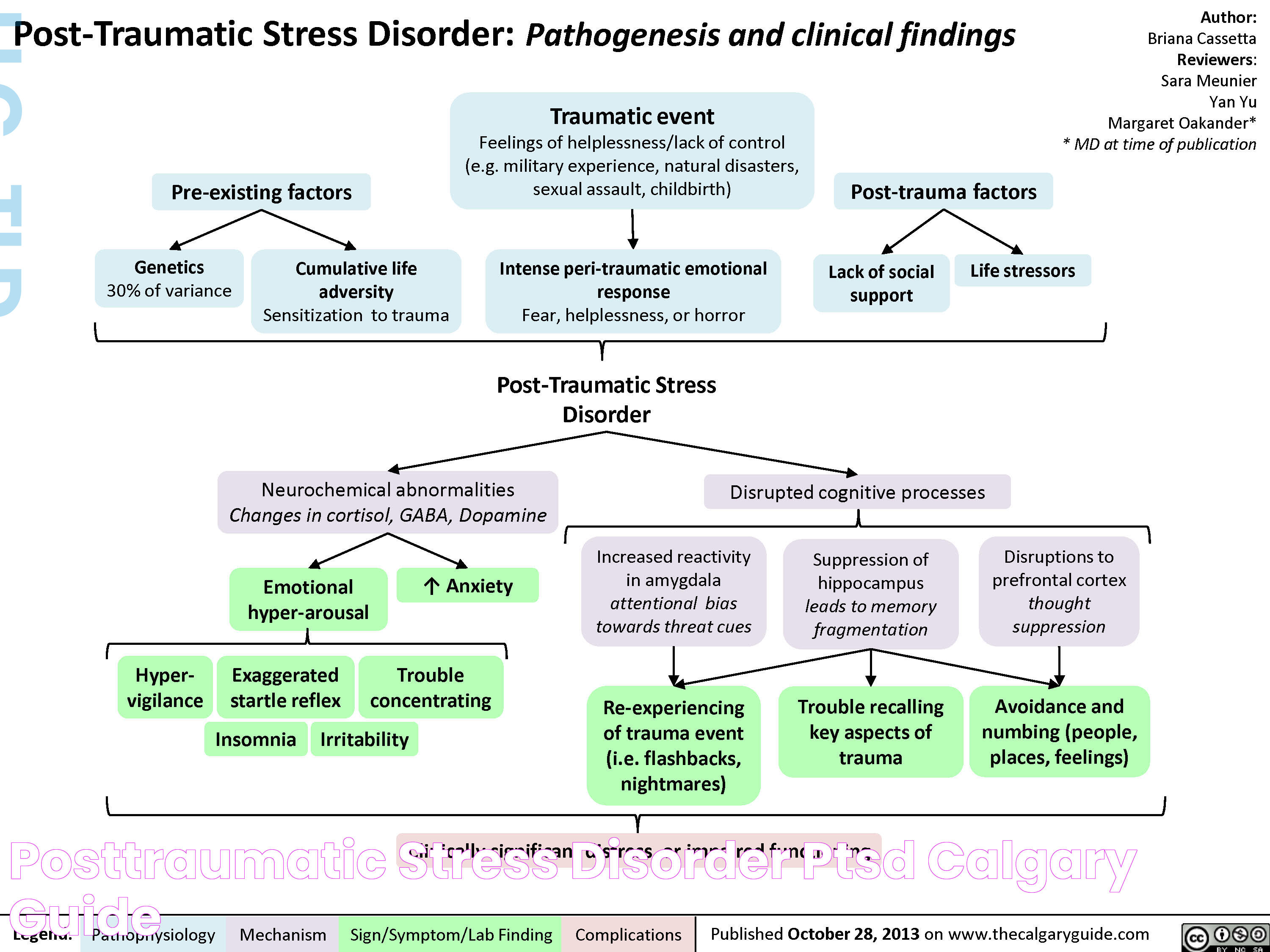
Traumatic disorder is a term that encompasses a range of mental health conditions triggered by experiencing or witnessing distressing events. These disorders can significantly impact an individual's emotional and psychological well-being, influencing their ability to function effectively in daily life. The journey to understanding and managing traumatic disorders is complex, requiring a multifaceted approach that addresses the unique needs of each individual. With the right support and interventions, individuals can find pathways to healing and recovery, reclaiming their lives from the shadows of trauma.
In recent years, increased awareness and research into traumatic disorders have shed light on the profound effects these conditions can have on individuals and communities. From post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) to acute stress responses, the spectrum of traumatic disorders is vast and varied. Each disorder presents its own set of challenges, symptoms, and treatment requirements, emphasizing the need for personalized care. This article delves into the intricacies of traumatic disorders, exploring their causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options, while highlighting the importance of empathy and understanding in the recovery process.
As society becomes more attuned to the mental health challenges faced by individuals with traumatic disorders, it is crucial to foster environments that support open dialogue and destigmatize mental health issues. By doing so, we can create spaces where individuals feel safe to seek help and share their experiences. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of traumatic disorders, offering insights into the latest research, expert opinions, and practical strategies for managing these complex conditions. Whether you are seeking information for yourself or a loved one, our goal is to empower you with knowledge and understanding.
Read also:Comprehensive Kyrie Irving Stats Analysis Career Highlights And Achievements
Table of Contents
- What is Traumatic Disorder?
- Causes of Traumatic Disorder
- Types of Traumatic Disorders
- Symptoms and Signs
- How Does Traumatic Disorder Affect Daily Life?
- Diagnosis and Assessment
- Treatment Options for Traumatic Disorder
- Therapy and Counseling
- Medication and Alternative Treatments
- Coping Strategies and Self-care
- The Role of Support Systems
- Can Traumatic Disorder Be Prevented?
- Living with Traumatic Disorder
- Future Directions in Traumatic Disorder Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Traumatic Disorder?
Traumatic disorder refers to a category of mental health conditions that arise after an individual experiences or witnesses a terrifying or life-threatening event. These disorders are characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can disrupt an individual's emotional, mental, and physical well-being. Traumatic disorders can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, and they often require professional intervention to manage effectively.
Traumatic disorders are typically associated with a traumatic event or series of events that overwhelm an individual's ability to cope. Such events may include natural disasters, accidents, war or combat experiences, abuse, or witnessing violence. The impact of these events can be profound, leading to lasting changes in the way individuals perceive and interact with the world around them. Understanding the nature of traumatic disorders is the first step in addressing their effects and supporting those affected.
Individuals with traumatic disorders often experience a range of symptoms that can include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the traumatic event. These symptoms can interfere with daily life, making it difficult for individuals to maintain relationships, perform tasks, or engage in activities they once enjoyed. Recognizing these symptoms and seeking help early can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with traumatic disorders.
Causes of Traumatic Disorder
The development of traumatic disorder is complex and multifaceted, often resulting from a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. While the specific causes can vary from one individual to another, several common elements contribute to the onset of traumatic disorders.
Genetic Factors
Research has suggested that genetics can play a role in the susceptibility to traumatic disorders. Individuals with a family history of mental health conditions may have a higher risk of developing a traumatic disorder following exposure to a traumatic event. Genetic predisposition can influence how the brain processes stress and fear responses, making some individuals more vulnerable to the effects of trauma.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, including the nature and severity of the traumatic event, can also contribute to the development of traumatic disorders. Individuals who experience repeated or prolonged exposure to trauma, such as in cases of chronic abuse or war, may be at a greater risk. Additionally, a lack of social support or exposure to high-stress environments can exacerbate the impact of trauma.
Read also:How Many People Can You Gameshare With On Ps5 A Comprehensive Guide
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, such as pre-existing mental health conditions, personality traits, and coping mechanisms, can influence an individual's response to trauma. People who struggle with anxiety, depression, or other mental health disorders may find it more challenging to process traumatic experiences. Similarly, individuals with limited coping skills or negative thinking patterns may be more susceptible to the effects of trauma.
Understanding the causes of traumatic disorders is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By identifying the factors that contribute to the development of these disorders, mental health professionals can tailor interventions to address the unique needs of each individual, improving their chances of recovery and resilience.
Types of Traumatic Disorders
Traumatic disorders encompass a wide range of conditions, each with its own unique characteristics and symptoms. While all traumatic disorders share a common link to distressing events, they differ in terms of their onset, duration, and impact on an individual's life. Some of the most common types of traumatic disorders include:
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is perhaps the most well-known type of traumatic disorder. PTSD can develop after an individual experiences or witnesses a traumatic event, such as combat, natural disasters, accidents, or assault. Symptoms of PTSD can include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and avoidance of situations that remind the individual of the trauma.
Acute Stress Disorder (ASD)
Acute Stress Disorder is characterized by the development of severe anxiety and dissociative symptoms within a short period following a traumatic event. Unlike PTSD, which can persist for months or years, ASD symptoms typically appear within days or weeks of the trauma and may resolve on their own. However, if left untreated, ASD can progress to PTSD.
Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (C-PTSD)
Complex PTSD is a condition that can arise from prolonged or repeated exposure to trauma, such as in cases of ongoing abuse or captivity. Individuals with C-PTSD may experience symptoms similar to PTSD, along with additional challenges such as emotional dysregulation, difficulty maintaining relationships, and negative self-perception.
Adjustment Disorder
Adjustment Disorder occurs when an individual experiences a significant emotional or behavioral response to a stressful life event, such as a divorce, job loss, or major life change. While these events may not be as overtly traumatic as others, the individual's reaction can lead to significant distress and impairment in daily functioning.
By understanding the different types of traumatic disorders, mental health professionals can provide more targeted and effective treatment options, helping individuals find relief from their symptoms and regain control over their lives.
Symptoms and Signs
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of traumatic disorders is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. While symptoms can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the disorder, several common indicators may suggest the presence of a traumatic disorder.
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms
- Intrusive thoughts or memories of the traumatic event
- Intense fear, anxiety, or panic attacks
- Feelings of hopelessness, sadness, or depression
- Emotional numbness or detachment from others
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
Behavioral Symptoms
- Avoidance of places, people, or activities that trigger memories of the trauma
- Changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia or nightmares
- Irritability, anger, or aggressive behavior
- Social withdrawal or isolation from friends and family
- Substance abuse or self-destructive behaviors
Physical Symptoms
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- Increased startle response or hypervigilance
- Headaches, stomachaches, or other unexplained physical symptoms
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Increased heart rate or palpitations
It is important to note that the presence of these symptoms alone does not necessarily indicate a traumatic disorder. However, if symptoms persist for an extended period and interfere with daily functioning, it may be beneficial to seek professional assessment and support. Early intervention can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
How Does Traumatic Disorder Affect Daily Life?
Traumatic disorders can have a profound impact on an individual's daily life, affecting their ability to function effectively in various areas. The effects of traumatic disorders can extend beyond the individual, influencing their relationships, work, and overall well-being.
Impact on Relationships
Individuals with traumatic disorders may struggle to maintain healthy relationships due to emotional numbness, withdrawal, or irritability. They may find it challenging to express their emotions or communicate effectively with loved ones, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts. Additionally, the avoidance of certain places or activities can limit social interactions and contribute to feelings of isolation.
Challenges in the Workplace
The symptoms of traumatic disorders can interfere with an individual's ability to perform effectively in the workplace. Difficulties with concentration, decision-making, and memory can impact job performance, while anxiety and stress may lead to increased absenteeism or difficulty meeting deadlines. For some individuals, workplace environments may trigger memories of the trauma, further complicating their ability to work.
Effects on Physical Health
Traumatic disorders can also have physical health implications, as chronic stress and anxiety can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of various health conditions. Individuals may experience sleep disturbances, changes in appetite, and unexplained physical symptoms, all of which can contribute to a decline in overall health and well-being.
Understanding the ways in which traumatic disorders affect daily life is essential for providing effective support and interventions. By addressing the unique challenges faced by individuals with these disorders, mental health professionals can help them develop coping strategies and find pathways to recovery.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis and assessment are critical steps in the treatment of traumatic disorders. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional can help identify the specific disorder, understand its severity, and determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
Clinical Interviews
Clinical interviews are a key component of the diagnostic process, allowing mental health professionals to gather detailed information about the individual's symptoms, history, and experiences. These interviews may include questions about the traumatic event, the individual's emotional and behavioral responses, and any previous mental health issues.
Psychological Assessments
Psychological assessments, such as standardized questionnaires and tests, can provide valuable insights into the individual's mental health status. These assessments may evaluate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and PTSD, helping clinicians to identify patterns and determine the severity of the disorder.
Medical Evaluations
In some cases, medical evaluations may be necessary to rule out any underlying physical conditions that could be contributing to the symptoms. This may involve a physical examination, laboratory tests, or imaging studies to identify any potential medical issues.
Once a diagnosis is made, the mental health professional can work with the individual to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Early and accurate diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes and help individuals regain control over their lives.
Treatment Options for Traumatic Disorder
Treating traumatic disorders requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the psychological and physical aspects of the condition. Mental health professionals may utilize a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle interventions to help individuals manage their symptoms and work toward recovery.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a widely used form of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. CBT can help individuals with traumatic disorders develop coping strategies, manage anxiety, and reduce the impact of traumatic memories.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR is a specialized therapeutic technique that aims to help individuals process and integrate traumatic memories. Through guided eye movements, individuals can reprocess distressing memories, reducing their emotional intensity and impact on daily life.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of traumatic disorders. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and mood stabilizers can be effective in reducing symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and art therapy, can complement traditional treatment approaches and provide additional support for individuals with traumatic disorders. These therapies can promote relaxation, enhance self-awareness, and improve emotional regulation.
The most effective treatment plans are those that are tailored to the individual's unique needs and preferences. By working collaboratively with mental health professionals, individuals can explore different treatment options and find the approaches that work best for them.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling are fundamental components of the treatment process for traumatic disorders. These interventions provide individuals with a safe and supportive environment to explore their experiences, learn coping skills, and work toward healing and recovery.
Individual Therapy
Individual therapy involves one-on-one sessions with a mental health professional, allowing individuals to discuss their thoughts, feelings, and experiences in a confidential setting. This personalized approach can help individuals gain insight into their symptoms, develop coping strategies, and work through unresolved trauma.
Group Therapy
Group therapy provides individuals with the opportunity to connect with others who have experienced similar challenges. In a group setting, individuals can share their experiences, learn from others, and receive support from peers. Group therapy can help reduce feelings of isolation and promote a sense of community and understanding.
Family Therapy
Family therapy involves working with family members to address the impact of traumatic disorders on family dynamics and relationships. This approach can enhance communication, improve understanding, and foster a supportive environment for the individual with the disorder.
Therapy and counseling play a vital role in the recovery process, helping individuals navigate the challenges of traumatic disorders and build a foundation for long-term well-being.
Medication and Alternative Treatments
Medication and alternative treatments can be valuable components of a comprehensive treatment plan for traumatic disorders. These interventions can address both the physiological and emotional aspects of the condition, providing individuals with additional tools for managing their symptoms.
Medication
- Antidepressants: These medications can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, improving mood and overall well-being.
- Anti-anxiety medications: These medications can reduce feelings of anxiety and panic, helping individuals manage stress and fear responses.
- Mood stabilizers: These medications can help regulate mood swings and reduce irritability, enhancing emotional stability.
Alternative Treatments
- Mindfulness meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help individuals develop greater self-awareness and reduce stress and anxiety.
- Yoga: Yoga can promote relaxation, improve physical health, and enhance emotional regulation.
- Art therapy: Art therapy provides a creative outlet for individuals to express their emotions and process trauma.
By incorporating a combination of medication and alternative treatments, individuals with traumatic disorders can address their symptoms more holistically and enhance their overall quality of life.
Coping Strategies and Self-care
Developing effective coping strategies and practicing self-care are essential components of managing traumatic disorders. These approaches can empower individuals to take an active role in their recovery and enhance their resilience in the face of challenges.
Coping Strategies
- Journaling: Writing about thoughts and feelings can help individuals process emotions and gain insight into their experiences.
- Relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can reduce stress and promote calmness.
- Creating a routine: Establishing a structured daily routine can provide a sense of stability and predictability, reducing anxiety and stress.
Self-care Practices
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can improve mood, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
- Healthy eating: A balanced diet can support physical and mental health, providing the nutrients needed for optimal functioning.
- Quality sleep: Prioritizing sleep and establishing a consistent sleep schedule can improve energy levels and mood.
By incorporating these coping strategies and self-care practices into their daily lives, individuals with traumatic disorders can build resilience and enhance their overall quality of life.
The Role of Support Systems
Support systems play a crucial role in the recovery process for individuals with traumatic disorders. Having a network of supportive friends, family members, and mental health professionals can provide individuals with the encouragement and resources needed to navigate the challenges of their condition.
Family and Friends
Family and friends can provide emotional support, understanding, and encouragement to individuals with traumatic disorders. By offering a listening ear, validating feelings, and expressing empathy, loved ones can help reduce feelings of isolation and foster a sense of connection and belonging.
Support Groups
Support groups provide individuals with the opportunity to connect with others who have experienced similar challenges. In a group setting, individuals can share their experiences, learn from others, and receive support from peers. Support groups can help reduce feelings of isolation and promote a sense of community and understanding.
Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals, such as therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists, play a vital role in providing support and guidance to individuals with traumatic disorders. These professionals can offer evidence-based treatments, coping strategies, and resources to help individuals manage their symptoms and work toward recovery.
By building and maintaining strong support systems, individuals with traumatic disorders can enhance their resilience and improve their overall quality of life.
Can Traumatic Disorder Be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all instances of traumatic disorders, there are steps individuals and communities can take to reduce the risk and impact of trauma. Prevention efforts focus on building resilience, providing early intervention, and creating supportive environments for individuals who have experienced trauma.
Building Resilience
Resilience refers to an individual's ability to adapt to and recover from adversity. By developing resilience, individuals can better cope with stress and trauma, reducing the likelihood of developing a traumatic disorder. Building resilience can involve developing strong social connections, practicing self-care, and fostering a positive outlook.
Early Intervention
Early intervention can help individuals process and manage their responses to traumatic events, reducing the risk of developing a traumatic disorder. Providing support and resources soon after a traumatic event can help individuals cope with their emotions and develop effective coping strategies.
Creating Supportive Environments
Creating supportive environments in schools, workplaces, and communities can help individuals feel safe and supported, reducing the impact of trauma. By promoting open dialogue, reducing stigma, and providing access to mental health resources, communities can create environments that support healing and resilience.
While it may not be possible to prevent all instances of traumatic disorders, these prevention efforts can help reduce the risk and impact of trauma, enhancing the well-being of individuals and communities.
Living with Traumatic Disorder
Living with a traumatic disorder can present many challenges, but with the right support and strategies, individuals can find ways to manage their symptoms and live fulfilling lives. By taking an active role in their recovery and seeking out resources and support, individuals with traumatic disorders can work toward healing and resilience.
Embracing Treatment and Support
Engaging with treatment and support is a crucial step in managing a traumatic disorder. By working with mental health professionals, individuals can explore different treatment options, develop coping strategies, and gain insight into their experiences. Building strong support systems with family, friends, and support groups can also provide encouragement and understanding.
Focusing on Self-care
Prioritizing self-care is essential for individuals living with traumatic disorders. By practicing self-care, individuals can enhance their physical and mental well-being, reducing stress and promoting resilience. Self-care practices can include regular exercise, healthy eating, relaxation techniques, and quality sleep.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals can help individuals with traumatic disorders focus on their progress and celebrate their achievements. By breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable steps, individuals can work toward their aspirations while maintaining a sense of control and accomplishment.
Living with a traumatic disorder requires patience, determination, and support. By embracing treatment, focusing on self-care, and setting realistic goals, individuals can find pathways to healing and resilience.
Future Directions in Traumatic Disorder Research
Research into traumatic disorders continues to evolve, offering new insights and potential treatment options for individuals affected by these conditions. As our understanding of traumatic disorders grows, researchers are exploring innovative approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Advancements in Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), are providing valuable insights into the brain's response to trauma. By studying brain activity and structure, researchers can identify patterns associated with traumatic disorders and develop targeted interventions to address these changes.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine aims to tailor treatment approaches to the unique needs and characteristics of each individual. By considering genetic, environmental, and psychological factors, researchers can develop more effective and personalized treatment plans for individuals with traumatic disorders.
Integrative Approaches
Integrative approaches that combine traditional and alternative therapies are gaining traction in the treatment of traumatic disorders. By exploring the potential benefits of therapies such as mindfulness, yoga, and art therapy, researchers are expanding the range of options available to individuals with these conditions.
As research into traumatic disorders continues to advance, there is hope for new and innovative approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By staying informed about the latest research and developments, individuals and mental health professionals can work together to improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for those affected by traumatic disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between PTSD and Acute Stress Disorder?
PTSD and Acute Stress Disorder (ASD) are both responses to traumatic events, but they differ in terms of duration and onset. ASD symptoms typically appear within days or weeks of the trauma and may resolve on their own, while PTSD symptoms can persist for months or years if left untreated.
Can children develop traumatic disorders?
Yes, children can develop traumatic disorders following exposure to distressing events. Children may exhibit symptoms such as nightmares, irritability, and changes in behavior. Early intervention and support are crucial for helping children process and cope with trauma.
How can I support a loved one with a traumatic disorder?
Supporting a loved one with a traumatic disorder involves offering empathy, understanding, and encouragement. Listening without judgment, validating their feelings, and encouraging them to seek professional help can provide valuable support and foster a sense of connection.
Are there any alternative therapies for traumatic disorders?
Yes, alternative therapies such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and art therapy can complement traditional treatment approaches and provide additional support for individuals with traumatic disorders. These therapies can promote relaxation, enhance self-awareness, and improve emotional regulation.
Is it possible to recover completely from a traumatic disorder?
While recovery from a traumatic disorder is a unique and individual process, many individuals can achieve significant improvements in their symptoms and overall quality of life with the right support and treatment. Recovery may involve managing symptoms, building resilience, and developing healthy coping strategies.
Can traumatic disorders be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all instances of traumatic disorders, building resilience, providing early intervention, and creating supportive environments can help reduce the risk and impact of trauma. These efforts can enhance the well-being of individuals and communities.
Conclusion
Traumatic disorders are complex conditions that can have a profound impact on an individual's emotional, psychological, and physical well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these disorders is essential for providing effective support and interventions. By embracing a comprehensive approach that includes therapy, medication, and self-care, individuals with traumatic disorders can find pathways to healing and resilience.
Creating supportive environments and fostering open dialogue about mental health can help reduce stigma and encourage individuals to seek the help they need. As research continues to advance, there is hope for new and innovative approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By staying informed and proactive, we can work together to improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for those affected by traumatic disorders.
For those seeking more information or support, consider visiting the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) website, which offers resources and guidance on mental health conditions, including traumatic disorders.
Article Recommendations

