Understanding Why Your JAR File Doesn't Say Executable: Solutions And Insights
Java Archive (JAR) files are crucial for packaging Java applications and libraries. They allow developers to bundle multiple files into a single archive for easier distribution and execution. However, encountering a JAR file that doesn't indicate it's executable can halt a project's progress. While this might seem like a minor inconvenience, it can lead to significant delays, especially when deploying applications across different environments.
In this detailed guide, we'll explore various reasons your JAR file might not be executable, ranging from misconfigurations to platform-specific issues. We'll also provide step-by-step instructions on how you can make your JAR file executable, ensuring a hassle-free experience. Whether you're a seasoned developer or someone just getting started with Java, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to tackle this common problem head-on.
Table of Contents
- What is a JAR File?
- How Do JAR Files Work?
- Common Reasons Why JAR File is Not Executable
- How to Make a JAR File Executable?
- Checking Executable Permissions on Different Operating Systems
- What to Do If JAR File Still Doesn't Run?
- Troubleshooting JAR File Execution Issues
- Understanding the Manifest File
- Does JAR File Require Java Runtime Environment?
- How to Create an Executable JAR File Using an IDE?
- Are There Any Alternatives to JAR Files?
- Security Considerations for Executable JAR Files
- How to Share Executable JAR Files?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a JAR File?
A JAR (Java Archive) file is a package file format typically used to aggregate many Java class files and associated metadata and resources (text, images, etc.) into one file for distribution. JAR files are built on the ZIP format and have a .jar file extension. They are a fundamental part of Java applications, providing a standard way to distribute Java programs and libraries.
Read also:Emma Watson The Iconic Journey From Hermione Granger In Harry Potter
JAR files are not exclusive to Java applications. They can also contain other types of files, such as XML files, images, and audio files, which are necessary for the application to function. This versatility makes JAR files a popular choice for distributing Java applications.
One of the key features of JAR files is their ability to compress files, reducing the size of the application or library. This compression is crucial for efficient distribution, particularly over the internet. JAR files also support digital signatures, allowing developers to verify the integrity of the files and ensure they have not been tampered with.
How Do JAR Files Work?
JAR files work by bundling multiple files into a single archive, making it easier to distribute and deploy Java applications. When a JAR file is created, it includes a manifest file, which is a special file that contains information about the files within the archive. The manifest file is located in the META-INF directory within the JAR file.
The manifest file can specify a variety of information, including the entry point of the application (the class with the main method), the version of the application, and the libraries required to run the application. By specifying the entry point, the manifest file allows the JAR file to be run as an executable, provided the necessary permissions and runtime environment are in place.
To run a JAR file, the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) must be installed on the computer. The JRE provides the necessary libraries and environment required to execute Java applications. Once the JRE is installed, the user can run the JAR file using the command line or by double-clicking the file, depending on the operating system and file permissions.
Common Reasons Why JAR File is Not Executable
There are several reasons why a JAR file might not be executable. Understanding these reasons can help you troubleshoot the issue and ensure your JAR files run as expected.
Read also:Snapgod Izzy S A Deep Dive Into The Life And Legacy
Missing Main-Class Attribute
The most common reason a JAR file is not executable is the absence of the Main-Class attribute in the manifest file. This attribute specifies the class containing the main method, which serves as the entry point of the application. Without this attribute, the Java runtime does not know which class to execute, resulting in the JAR file not being executable.
To resolve this issue, you can manually edit the manifest file or recreate the JAR file with the correct Main-Class attribute. Most IDEs provide options to specify the main class when creating a JAR file, simplifying this process.
Incorrect File Permissions
Another common reason a JAR file is not executable is incorrect file permissions. On Unix-based systems, such as Linux and macOS, the executable bit must be set for the JAR file to be run as an executable. If this permission is not set, the operating system will not allow the JAR file to be executed, regardless of the contents of the manifest file.
To set the executable bit, you can use the chmod command in the terminal. For example, to make a JAR file executable, you can run the following command:
chmod +x filename.jarThis command sets the executable bit, allowing the JAR file to be run as an executable.
Platform-Specific Issues
Different operating systems have different methods of handling executable files, which can lead to platform-specific issues when running JAR files. For example, on Windows, the Java Runtime Environment must be correctly installed, and the .jar file extension must be associated with the Java runtime. If these conditions are not met, the JAR file may not be executable.
On macOS and Linux, the file permissions and the presence of a correct Java installation are critical. Ensuring the Java runtime is installed and configured correctly can help address these platform-specific issues.
How to Make a JAR File Executable?
Making a JAR file executable involves several steps, including ensuring the correct manifest file configuration and setting appropriate file permissions. Follow these steps to make your JAR file executable:
- Create the Manifest File: Ensure your manifest file includes the Main-Class attribute, specifying the class containing the main method. You can create or edit the manifest file manually or specify the main class when building the JAR file using an IDE or build tool like Maven or Gradle.
- Build the JAR File: Use a build tool or IDE to package your Java application into a JAR file. Ensure the manifest file is included in the JAR file.
- Set File Permissions: On Unix-based systems, set the executable bit for the JAR file using the chmod command:
- Ensure Java is Installed: Verify that the Java Runtime Environment is installed on the target system. This step is crucial for executing JAR files.
- Run the JAR File: Once the above steps are completed, you can run the JAR file using the command line or by double-clicking the file, depending on the operating system and file permissions.
chmod +x filename.jarChecking Executable Permissions on Different Operating Systems
Executable permissions vary across different operating systems. Understanding how each system handles these permissions can help ensure your JAR files run smoothly.
Windows
On Windows, executable permissions are not typically an issue for JAR files. Instead, ensure the Java Runtime Environment is installed and the .jar file extension is associated with the Java runtime. To associate the .jar extension, you may need to adjust the system settings or reinstall the JRE.
macOS and Linux
On macOS and Linux, the executable bit must be set for the JAR file. Use the chmod command to set this permission. Additionally, ensure the Java runtime is correctly installed and configured. You can check the Java installation by running the following command in the terminal:
java -versionThis command displays the installed Java version, confirming the runtime is available.
What to Do If JAR File Still Doesn't Run?
If your JAR file still doesn't run after setting the correct permissions and ensuring the Java runtime is installed, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check the Manifest File: Verify the manifest file is correctly configured with the Main-Class attribute.
- Rebuild the JAR File: Recreate the JAR file, ensuring the manifest file is included and correctly configured.
- Review Error Messages: When attempting to run the JAR file, review any error messages displayed in the terminal or command prompt. These messages can provide valuable insights into the underlying issue.
- Consult Documentation: Review the documentation for your build tool or IDE for additional guidance on creating executable JAR files.
Troubleshooting JAR File Execution Issues
Troubleshooting JAR file execution issues requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the problem. Consider the following troubleshooting tips:
- Verify the Java Installation: Ensure the Java Runtime Environment is correctly installed and configured.
- Check File Permissions: Confirm the JAR file has the necessary executable permissions.
- Review the Manifest File: Verify the manifest file is correctly formatted and includes the Main-Class attribute.
- Test on a Different System: If possible, test the JAR file on a different system to determine if the issue is system-specific.
- Search Online Resources: Consult online forums, documentation, and resources for additional troubleshooting tips and solutions.
Understanding the Manifest File
The manifest file is a critical component of a JAR file, providing essential metadata about the files within the archive. Understanding how to configure the manifest file is crucial for creating executable JAR files.
Key Attributes
Several key attributes can be specified in the manifest file, including:
- Main-Class: Specifies the class containing the main method, serving as the entry point of the application.
- Class-Path: Lists the libraries required to run the application.
- Version: Specifies the version of the application or library.
- Signature: Provides a digital signature to verify the integrity of the files.
Creating a Manifest File
To create a manifest file, you can use a text editor to write the desired attributes, then include the file in the JAR archive. Most build tools and IDEs offer options to automatically generate and include a manifest file when building a JAR file.
Does JAR File Require Java Runtime Environment?
Yes, a JAR file requires the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) to be installed on the target system. The JRE provides the necessary libraries and environment required to execute Java applications packaged within the JAR file.
Why is JRE Important?
The JRE is important because it provides the runtime environment for executing Java applications. It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), core libraries, and other components necessary to run Java applications. Without the JRE, the system cannot interpret and execute the Java bytecode contained within the JAR file.
To ensure your JAR file runs correctly, verify the JRE is installed and configured on the target system. You can download the JRE from the official Oracle website or use an open-source alternative like OpenJDK.
How to Create an Executable JAR File Using an IDE?
Creating an executable JAR file using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) simplifies the process, providing a user-friendly interface and automated tools to package your Java application efficiently. Follow these steps to create an executable JAR file using popular IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse:
Using IntelliJ IDEA
- Open your Java project in IntelliJ IDEA.
- Navigate to File >Project Structure.
- Under the Artifacts section, click + to add a new artifact and select JAR > From modules with dependencies.
- Specify the main class in the dialog box and click OK.
- Click Build >Build Artifacts >Build to create the JAR file.
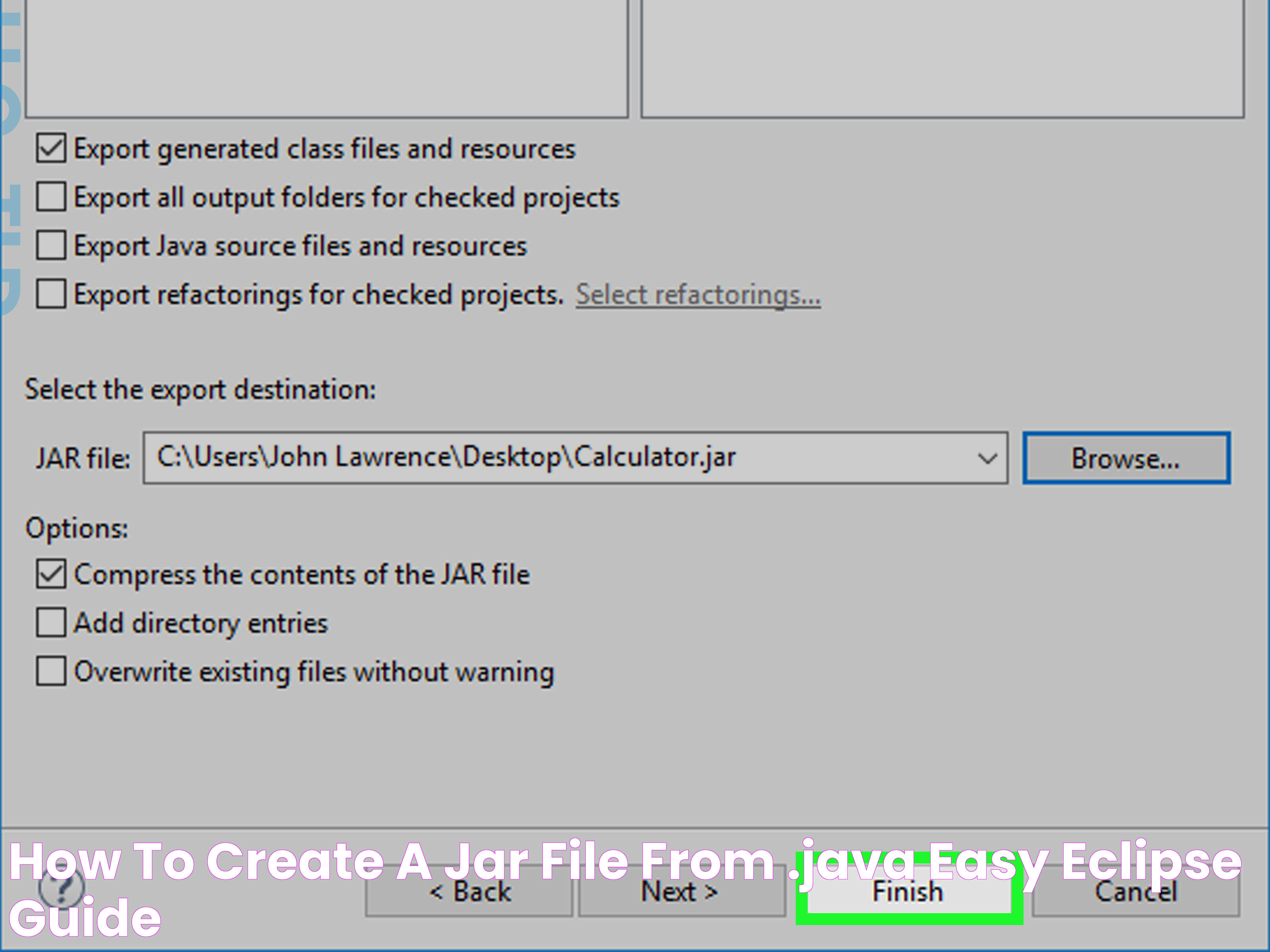
Using Eclipse
- Open your Java project in Eclipse.
- Right-click the project in the Package Explorer and select Export.
- Choose Java >Runnable JAR file and click Next.
- Select the launch configuration and specify the export destination.
- Click Finish to create the JAR file.
Both IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse provide intuitive interfaces, making it easy to configure the manifest file and set the main class for your executable JAR file.
Are There Any Alternatives to JAR Files?
While JAR files are the standard format for distributing Java applications, there are alternatives that may be better suited for specific use cases. Consider the following alternatives:
WAR Files
WAR (Web Application Archive) files are used to package web applications for deployment on servers that support the Java EE (Enterprise Edition) platform. They contain JSP files, servlets, XML files, and other components required for web applications.
EAR Files
EAR (Enterprise Archive) files are used to package entire enterprise applications, including EJB modules, web modules, and resource adapters. EAR files are suitable for larger applications that require multiple modules and components.
Executable JARs
Executable JARs are JAR files that include a manifest file specifying the main class and necessary libraries, allowing them to be run directly without additional configuration. They are an alternative to traditional JAR files for standalone applications.
Security Considerations for Executable JAR Files
Security is a critical consideration when distributing and executing JAR files. Taking steps to ensure your JAR files are secure can protect your applications and users from potential threats.
Digital Signatures
Using digital signatures allows you to verify the integrity and authenticity of your JAR files. A digital signature confirms that the files have not been altered and that they originate from a trusted source. Consider using a code-signing certificate to digitally sign your JAR files.
Code Obfuscation
Code obfuscation is a technique used to make the source code within your JAR files more difficult to understand, protecting your intellectual property and preventing reverse engineering. Consider using obfuscation tools to protect sensitive code and algorithms.
Additionally, ensure your JAR files are distributed securely, using trusted platforms and secure protocols to prevent unauthorized access and distribution.
How to Share Executable JAR Files?
Sharing executable JAR files involves distributing them to users or systems that require access to your application. Consider the following methods for sharing JAR files:
Via Email or Messaging Platforms
For small JAR files, consider sharing them via email or messaging platforms. Ensure the recipient has the necessary permissions and runtime environment to execute the JAR file.
Using Cloud Storage Services
Cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive provide a convenient way to share larger JAR files. Share the download link with users, ensuring they have access to the cloud storage service.
Through a Version Control System
Version control systems like GitHub or GitLab allow you to share JAR files with developers and collaborators. Create a repository for your project and include the JAR file in the repository for easy access and version control.
On a Dedicated Website or FTP Server
If you have a dedicated website or FTP server, consider hosting the JAR file for easy download. Ensure the server is secure and accessible to authorized users.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why doesn't my JAR file say executable?
Your JAR file might not be executable due to a missing or incorrect Main-Class attribute in the manifest file, incorrect file permissions, or platform-specific issues. Ensure the manifest file is properly configured, set the correct file permissions, and verify the Java runtime is installed.
2. How do I set the executable bit for a JAR file on Linux?
Use the chmod command to set the executable bit for a JAR file on Linux. Run the following command in the terminal: chmod +x filename.jar. This command sets the executable bit, allowing the JAR file to be run as an executable.
3. Can I run a JAR file without the Java Runtime Environment?
No, a JAR file requires the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) to be installed on the system. The JRE provides the necessary libraries and environment to execute Java applications.
4. What should I include in the manifest file to make a JAR file executable?
To make a JAR file executable, include the Main-Class attribute in the manifest file, specifying the class containing the main method. This attribute directs the Java runtime to the entry point of the application.
5. How do I troubleshoot a JAR file that won't execute on Windows?
On Windows, ensure the Java Runtime Environment is installed and the .jar file extension is associated with the Java runtime. Verify the manifest file is correctly configured and review any error messages for additional insights.
6. Are there any security risks associated with running JAR files?
Running JAR files from untrusted sources can pose security risks. Always verify the authenticity and integrity of JAR files before execution. Consider using digital signatures and code obfuscation to enhance security when distributing JAR files.
Conclusion
Understanding why your JAR file doesn't say executable is essential for smooth Java application development and deployment. By identifying common issues, such as missing manifest attributes or incorrect file permissions, and following the outlined solutions, you can ensure your JAR files are executable across different platforms. Remember to prioritize security by using digital signatures and secure distribution methods, and always verify the Java runtime environment is properly installed on target systems. With these insights and solutions, you're well-equipped to tackle JAR file execution issues and optimize your Java application's performance.
Article Recommendations

