The Intriguing World Of Cockroaches: Can They Really Live In Your Body?
In the realm of urban myths and unsettling tales, few creatures inspire as much fear and fascination as the cockroach. The mere thought of these resilient insects is enough to make one's skin crawl, especially when pondering the question: can cockroaches live in your body? While it may sound like a plot twist from a horror film, this query has captured the imaginations of many and sparked curiosity about the capabilities and behaviors of these notorious critters.
Despite their reputation, cockroaches are not inherently interested in becoming internal residents of the human body. These creatures thrive in environments where food, water, and shelter are readily available, typically steering clear of the inhospitable human interior. However, there have been rare instances where cockroaches have accidentally entered human bodies, usually gaining access through the ears or nose. Such occurrences, though unsettling, are exceptions rather than the norm.
This article delves into the biology and behavior of cockroaches, exploring their preferred habitats, survival mechanisms, and the potential risks they pose to humans. By understanding the nature of these insects, we can dispel myths and gain a clearer insight into whether or not cockroaches can truly live in your body. Join us as we embark on this informative journey into the world of cockroaches, separated from fiction and grounded in scientific understanding.
Read also:The Parthenon A Timeless Marvel Of Ancient Greece
Table of Contents
- Biology of Cockroaches: Nature's Survivors
- Can Cockroaches Live in Your Body?
- Cockroach Habitats and Preferences
- How Do Cockroaches Survive?
- Health Risks Associated with Cockroaches
- Cockroach Infestation Prevention
- Cockroach Removal Methods
- Why Are Cockroaches So Resilient?
- Cockroach Myths Debunked
- What If a Cockroach Enters Your Body?
- Can Cockroaches Cause Serious Health Issues?
- Interesting Facts About Cockroaches
- Cockroach Studies and Research
- How to Handle Cockroach Encounters?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Biology of Cockroaches: Nature's Survivors
Cockroaches are one of the oldest living species on the planet, with a lineage tracing back over 300 million years. Their survival through epochs of environmental changes is a testament to their adaptability and resilience. There are approximately 4,500 species of cockroaches, but only about 30 are considered pests. The most common species that people encounter include the German, American, and Oriental cockroaches.
These insects are part of the order Blattodea and are closely related to termites. Cockroaches are characterized by their flattened bodies, long antennae, and the ability to run quickly. They possess a tough exoskeleton that provides protection and aids in their survival across various environments. Cockroaches are nocturnal creatures, preferring to remain hidden during the day and emerging at night to forage for food.
Their diet is omnivorous, meaning they consume a wide range of organic materials. This includes decaying matter, food scraps, and even paper products. Cockroaches are equipped with strong jaws that enable them to chew through tough materials. Their digestive system is highly efficient, allowing them to extract nutrients from seemingly inedible substances.
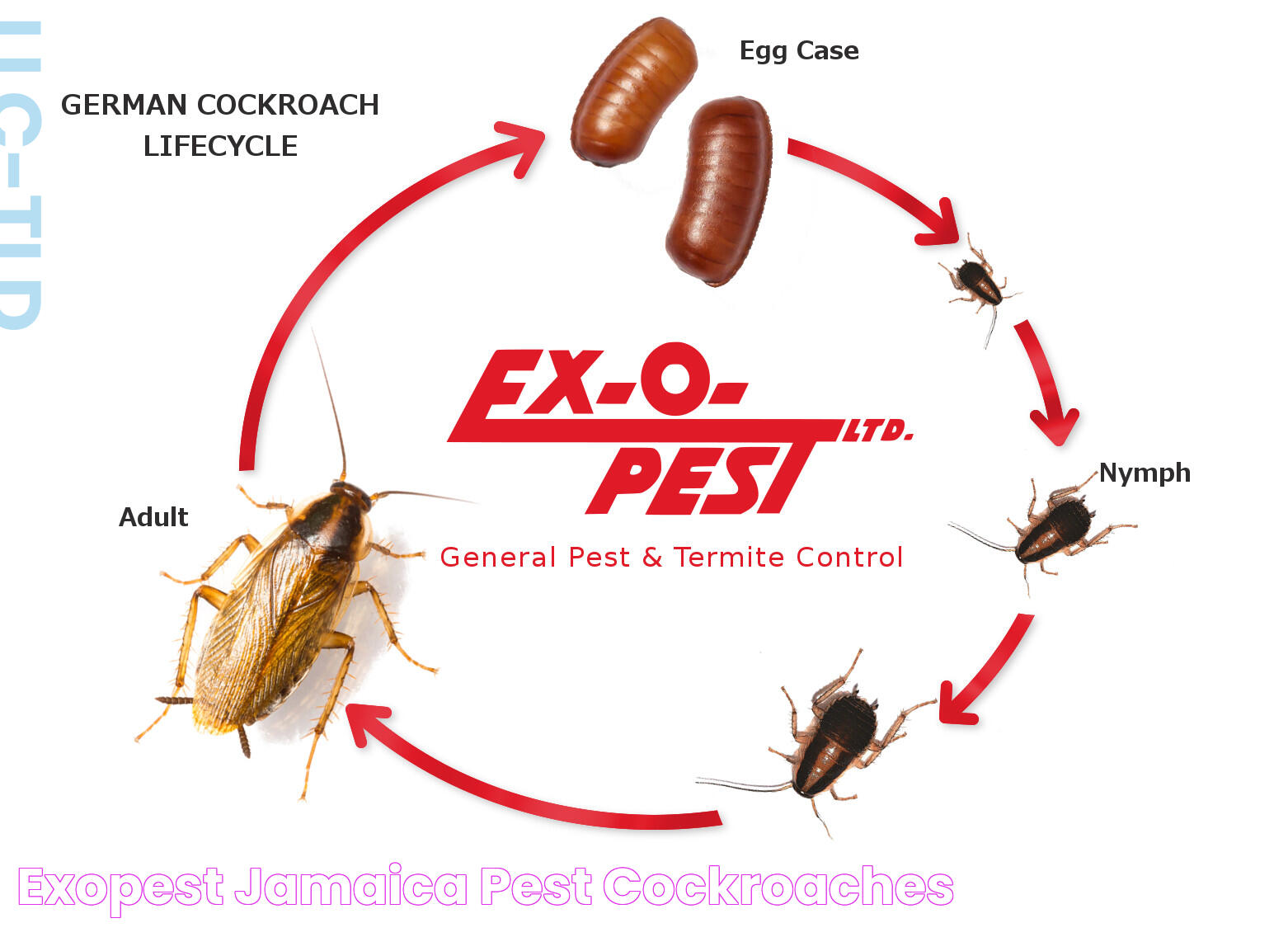
The reproductive capacity of cockroaches is remarkable, contributing to their success as a species. Female cockroaches produce egg cases known as oothecae, which contain multiple eggs. These egg cases are often deposited in hidden locations, ensuring the safety of the developing embryos. Once hatched, nymphs undergo a series of molts before reaching adulthood, with each stage bringing them closer to reproductive maturity.
Can Cockroaches Live in Your Body?
The notion that cockroaches can live inside the human body is a pervasive urban legend, fueled by the fear of these insects and their invasive nature. However, the reality is far less dramatic. Cockroaches are not parasitic and have no natural inclination to inhabit the human body. Their preferred environments are warm, humid spaces with access to food and water, such as kitchens and bathrooms.
While there have been rare reports of cockroaches entering human orifices, such as the ear canal, these instances are accidental and typically occur when a person is asleep. The warm, moist environment of the ear can attract cockroaches seeking shelter, but they do not survive or thrive in such conditions. Medical intervention is often required to remove the intruder and alleviate discomfort.
Read also:Insights Into Alexis Bledels Child A Look Into Her Family Life
It is important to note that cockroaches do not have the biological capability to live inside the human body for extended periods. The human immune system and the inhospitable internal environment make it impossible for cockroaches to establish residence. Furthermore, the instances of cockroach entry into the body are exceedingly rare and should not be a cause for widespread alarm.
The myth of cockroaches living in the body may stem from misunderstandings about their behavior and habitat preferences. By educating ourselves about these creatures, we can dispel fears and focus on effective prevention and control measures to keep our homes free from cockroach infestations.
Cockroach Habitats and Preferences
Cockroaches are highly adaptable insects, capable of thriving in a variety of environments. Their preferred habitats are warm, humid areas with ample food and water sources. This includes kitchens, bathrooms, basements, and sewers. In urban settings, cockroaches often find refuge in cracks, crevices, and cluttered spaces where they can remain hidden from predators and human activity.
The availability of food is a significant factor in determining cockroach habitats. These opportunistic feeders are drawn to areas where they can scavenge for scraps and waste. They are known to consume a wide range of organic materials, including food residues, grease, and decaying matter. Their ability to digest cellulose allows them to feed on paper products and even cardboard.
Cockroaches are nocturnal creatures, emerging at night to forage for food. During the day, they seek shelter in dark, undisturbed areas where they can rest and reproduce. This behavior makes them difficult to detect and control, as they often remain hidden during daylight hours.
Environmental conditions also play a role in cockroach habitat selection. These insects thrive in temperatures between 70 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit, making them more active during the warmer months. However, they are capable of surviving in a range of temperatures, allowing them to persist in various climates and regions.
Understanding cockroach habitats and preferences is essential for effective pest control. By identifying and eliminating potential food and water sources, as well as sealing entry points, homeowners can reduce the likelihood of cockroach infestations. Regular cleaning and maintenance can also help create an inhospitable environment for these unwelcome guests.
How Do Cockroaches Survive?
Cockroaches are renowned for their survival skills, earning them the reputation of being one of the most resilient creatures on Earth. Their ability to adapt to diverse environments and withstand harsh conditions is a testament to their evolutionary success. Several factors contribute to their remarkable survival capabilities.
One of the key elements of cockroach survival is their exoskeleton, which provides protection against physical harm and desiccation. This tough outer layer acts as a barrier, preventing water loss and allowing them to endure dry conditions. The exoskeleton also enables cockroaches to squeeze into tight spaces, aiding their escape from predators and enabling them to access food sources.
Cockroaches possess a highly efficient digestive system that allows them to extract nutrients from a wide range of organic materials. Their ability to digest cellulose enables them to consume paper products, wood, and even glue. This dietary flexibility ensures their survival in environments where traditional food sources are scarce.
Another survival mechanism is their rapid reproductive rate. Female cockroaches produce multiple egg cases, each containing several eggs. These egg cases are often deposited in hidden locations, ensuring the safety of the developing embryos. Once hatched, nymphs undergo a series of molts, rapidly reaching reproductive maturity and contributing to population growth.
Cockroaches are also able to survive without food for extended periods, relying on their fat reserves to sustain them during lean times. They can go without food for up to a month, although they do require access to water to survive. This ability allows them to persist in environments where food is scarce, increasing their chances of survival.
Ultimately, the resilience of cockroaches is a result of their adaptability, efficient resource utilization, and rapid reproduction. These traits have enabled them to thrive in a wide range of environments, making them one of the most successful species on the planet.
Health Risks Associated with Cockroaches
Cockroaches are more than just a nuisance; they pose significant health risks to humans. These insects are known carriers of various pathogens and allergens, contributing to the spread of disease and triggering allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
One of the primary health concerns associated with cockroaches is their role as vectors for disease-causing bacteria and viruses. As they scuttle across surfaces in search of food, cockroaches can pick up and transport harmful microorganisms, contaminating food and food preparation areas. Some of the pathogens associated with cockroaches include Salmonella, E. coli, and Staphylococcus. These bacteria can cause food poisoning, gastrointestinal infections, and other illnesses.
In addition to bacteria, cockroaches can also carry parasitic worms and fungi. Their ability to transmit these organisms increases the risk of infections and infestations in humans. The presence of cockroaches in homes and businesses can compromise sanitation and hygiene, resulting in health hazards for inhabitants and patrons.
Another significant health risk posed by cockroaches is their ability to trigger allergies and asthma. Cockroach saliva, feces, and body parts contain proteins that can act as allergens, inducing allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. Symptoms of cockroach allergies include sneezing, itchy eyes, skin rashes, and respiratory issues. For asthma sufferers, exposure to cockroach allergens can exacerbate symptoms and lead to asthma attacks.
The health risks associated with cockroaches underline the importance of effective pest control and prevention measures. By maintaining cleanliness, eliminating food and water sources, and sealing entry points, homeowners can reduce the risk of cockroach infestations and protect their health.
Cockroach Infestation Prevention
Preventing cockroach infestations requires a proactive approach that focuses on eliminating potential food, water, and shelter sources. By implementing effective prevention strategies, homeowners can reduce the likelihood of encountering these unwelcome pests.
One of the most effective ways to prevent cockroach infestations is to maintain a clean and clutter-free environment. Regular cleaning and sanitation are essential to remove food residues, grease, and crumbs that can attract cockroaches. Pay special attention to kitchens and bathrooms, as these areas are prime targets for cockroach activity.
Proper food storage is also crucial in preventing infestations. Store food in sealed containers and promptly clean up spills and crumbs. Avoid leaving pet food out overnight and regularly clean pet feeding areas to eliminate potential food sources for cockroaches.
Eliminating water sources is another important aspect of cockroach prevention. Fix leaky pipes and faucets, and ensure that sinks and tubs are dry before going to bed. Cockroaches are attracted to moisture, so reducing humidity levels can make your home less appealing to them.
Sealing entry points is an effective way to keep cockroaches out of your home. Inspect your property for cracks, crevices, and gaps around doors and windows, and seal them with caulk or weatherstripping. Installing door sweeps can also help prevent cockroaches from entering through gaps under doors.
Regular inspections and monitoring can help detect early signs of cockroach activity. Look for droppings, egg cases, and shed skins in areas where cockroaches are likely to hide. If you suspect an infestation, contact a professional pest control service to assess the situation and recommend appropriate treatment measures.
Cockroach Removal Methods
When faced with a cockroach infestation, swift and effective removal is essential to prevent the spread of these pests and the health risks they pose. There are several methods for cockroach removal, ranging from DIY approaches to professional pest control solutions.
One common DIY method for cockroach removal is the use of bait stations. These contain insecticide-laced bait that attracts cockroaches, which then consume the bait and return to their nests, spreading the poison to other members of the colony. Bait stations are effective for controlling small to moderate infestations and are available at most hardware stores.
Insecticide sprays and dusts are also commonly used for cockroach removal. These products can be applied to cracks, crevices, and other hiding places where cockroaches dwell. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and safety precautions when using these products to ensure effective and safe application.
For larger infestations, professional pest control services may be necessary. Pest control professionals have access to more potent insecticides and specialized equipment to effectively eliminate cockroaches. They can also provide guidance on preventive measures to reduce the risk of future infestations.
In addition to chemical methods, non-chemical approaches such as traps and exclusion techniques can be used to control cockroach populations. Sticky traps can capture cockroaches as they move about, helping to monitor and reduce their numbers. Exclusion techniques, such as sealing entry points and reducing clutter, can prevent cockroaches from entering and establishing themselves in your home.
Ultimately, the choice of cockroach removal method depends on the severity of the infestation and personal preferences. Combining multiple approaches can enhance effectiveness and ensure long-term control of cockroach populations.
Why Are Cockroaches So Resilient?
The resilience of cockroaches is a result of their evolutionary adaptations and biological traits that enable them to survive in a wide range of environments and conditions. Several factors contribute to their remarkable ability to withstand challenges and persist over time.
One key factor in cockroach resilience is their exoskeleton, which provides physical protection and helps prevent water loss. This tough outer layer shields cockroaches from predators, physical damage, and desiccation, allowing them to thrive in diverse environments.
Cockroaches are also highly adaptable when it comes to their diet. Their omnivorous nature allows them to consume a wide variety of organic materials, from food scraps to decaying matter. Their ability to digest cellulose enables them to feed on paper products and wood, ensuring their survival even in environments with limited food sources.
The reproductive capacity of cockroaches further enhances their resilience. With the ability to produce multiple egg cases containing numerous eggs, cockroaches can rapidly increase their populations. This reproductive strategy allows them to recover quickly from population declines and maintain their presence in various habitats.
Cockroaches are capable of surviving without food for extended periods, relying on their fat reserves to sustain them during times of scarcity. They can go without food for up to a month, although they require access to water to survive. This ability to endure periods of starvation contributes to their survival in challenging environments.
Their nocturnal behavior and preference for dark, hidden spaces make cockroaches difficult to detect and eliminate. By remaining concealed during the day and emerging at night to forage, they reduce their exposure to predators and human intervention.
Overall, the resilience of cockroaches is a result of their adaptability, efficient resource utilization, and rapid reproduction. These traits have enabled them to thrive in a wide range of environments, making them one of the most successful and persistent species on the planet.
Cockroach Myths Debunked
Cockroaches are often the subject of myths and misconceptions, fueled by their reputation as resilient and invasive pests. By debunking these myths, we can gain a clearer understanding of cockroach behavior and biology, and dispel unfounded fears.
One common myth is that cockroaches can survive a nuclear explosion. While cockroaches are more resistant to radiation than humans, they are not immune to its effects. High levels of radiation can still be lethal to cockroaches, although their ability to endure some exposure is due to their simple body structure and relatively slow cell division.
Another myth is that cockroaches can live without their heads indefinitely. While it's true that cockroaches can survive for a short period without their heads, this is due to their open circulatory system and the fact that they breathe through spiracles in their bodies. Without a head, cockroaches are unable to eat or drink, and they eventually die from dehydration.
There is also a misconception that cockroaches are indestructible. Though they are incredibly resilient, cockroaches are not invincible. They are susceptible to extreme temperatures, dehydration, and predation. Effective pest control measures can successfully eliminate cockroach infestations.
Some people believe that cockroaches are attracted to dirty homes. While clutter and food residues can attract cockroaches, they can also infest clean homes if there are accessible food and water sources. Cockroaches are opportunistic feeders and will seek out environments that provide the resources they need to survive.
Understanding the facts about cockroaches can help dispel myths and reduce fear and anxiety associated with these insects. By focusing on prevention and control measures, we can effectively manage cockroach populations and protect our homes from infestation.
What If a Cockroach Enters Your Body?
The thought of a cockroach entering the human body is unsettling, but such occurrences are rare and typically accidental. These incidents usually involve cockroaches entering the ear canal while a person is asleep, attracted by the warmth and moisture.
If a cockroach does enter the ear, it can cause discomfort, pain, and a sensation of fullness. In some cases, the insect may cause damage to the ear canal or eardrum if it moves around. It is important to seek medical attention promptly to safely remove the intruder and alleviate symptoms.
Medical professionals can remove cockroaches from the ear using specialized instruments or by flushing the ear canal with water or saline solution. Attempting to remove the insect yourself can be risky and may cause further injury to the ear.
Cockroaches are not capable of living or reproducing inside the human body, as the internal environment is inhospitable to them. The human immune system and bodily fluids create conditions that are unsuitable for cockroach survival.
While the idea of a cockroach entering the body is alarming, these incidents are rare and should not be a cause for widespread concern. Taking preventive measures, such as sealing entry points and reducing clutter, can help minimize the risk of cockroach encounters.
Can Cockroaches Cause Serious Health Issues?
Cockroaches are known to pose health risks to humans, primarily through the spread of pathogens and allergens. While they are not direct vectors of specific diseases, their presence can contribute to the transmission of harmful bacteria and viruses.
As cockroaches scuttle across surfaces, they can pick up and spread disease-causing microorganisms, contaminating food and food preparation areas. Some of the pathogens associated with cockroaches include Salmonella, E. coli, and Staphylococcus. These bacteria can lead to food poisoning, gastrointestinal infections, and other illnesses.
Cockroaches can also carry parasitic worms and fungi, increasing the risk of infections and infestations in humans. Their ability to transmit these organisms highlights the importance of maintaining cleanliness and hygiene to prevent cockroach infestations.
In addition to their role in disease transmission, cockroaches are significant contributors to indoor allergens. Their saliva, feces, and body parts contain proteins that can act as allergens, triggering allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Symptoms of cockroach allergies include sneezing, itchy eyes, skin rashes, and respiratory issues. For asthma sufferers, exposure to cockroach allergens can exacerbate symptoms and lead to asthma attacks.
While cockroaches are not directly responsible for causing serious health issues, their presence can compromise sanitation and hygiene, increasing the risk of illness and allergic reactions. Effective pest control measures and preventive strategies are essential to reduce the health risks associated with cockroaches.
Interesting Facts About Cockroaches
Cockroaches are fascinating creatures with unique biological traits and behaviors that have contributed to their success as a species. Here are some intriguing facts about these resilient insects:
- Cockroaches are ancient insects, with fossil evidence suggesting they have existed for over 300 million years, predating dinosaurs.
- There are approximately 4,500 species of cockroaches, but only about 30 are considered pests that commonly infest human dwellings.
- Cockroaches can hold their breath for up to 40 minutes, allowing them to survive in low-oxygen environments and withstand temporary submersion in water.
- These insects can run at speeds of up to 3 miles per hour, making them one of the fastest insects capable of escaping predators quickly.
- Cockroaches are highly adaptable and can survive in a wide range of temperatures, from freezing cold to extreme heat.
- Female cockroaches produce egg cases known as oothecae, which can contain up to 50 eggs, ensuring rapid population growth.
- Cockroaches can live for a week without their heads due to their open circulatory system and ability to breathe through spiracles in their bodies.
- These insects are capable of digesting cellulose, allowing them to feed on paper products, wood, and even glue.
Understanding these facts about cockroaches can help us appreciate their resilience and adaptability, while also highlighting the importance of effective pest control measures to manage their populations.
Cockroach Studies and Research
Scientific research on cockroaches has provided valuable insights into their biology, behavior, and impact on human health. Studies have focused on various aspects of cockroach ecology, physiology, and pest control strategies.
Research on cockroach behavior has revealed their complex social interactions and communication methods. These insects use pheromones to signal danger, find food, and attract mates. Understanding these communication mechanisms can inform the development of targeted pest control solutions.
Studies on cockroach physiology have explored their ability to withstand harsh conditions, including radiation and dehydration. Researchers have investigated the genetic and biological factors that contribute to their resilience, with implications for pest control and evolutionary biology.
Public health research has examined the role of cockroaches in disease transmission and allergen production. By identifying the specific pathogens and allergens associated with cockroaches, scientists can develop strategies to mitigate their impact on human health.
Advancements in pest control research have led to the development of more effective and environmentally friendly methods for managing cockroach populations. This includes the use of biological control agents, such as natural predators and pathogens, as well as the development of targeted baits and traps.
Overall, ongoing research on cockroaches continues to enhance our understanding of these insects and inform strategies for managing their populations and reducing their impact on human health and well-being.
How to Handle Cockroach Encounters?
Encountering a cockroach can be an unsettling experience, but knowing how to handle the situation can help reduce anxiety and ensure effective pest management. Here are some steps to take when dealing with cockroach encounters:
- Stay Calm: While cockroaches can be alarming, it's important to remain calm and avoid panicking. Remember that cockroaches are generally harmless and unlikely to cause immediate harm.
- Identify the Problem: Determine whether the encounter is a one-time occurrence or indicative of a larger infestation. Look for signs of cockroach activity, such as droppings, egg cases, and shed skins, to assess the severity of the problem.
- Take Preventive Measures: Implement preventive strategies to reduce the risk of further encounters. This includes eliminating food and water sources, sealing entry points, and maintaining a clean and clutter-free environment.
- Use Traps and Baits: Deploy sticky traps and bait stations to capture and control cockroach populations. These products can help monitor and reduce the number of cockroaches in your home.
- Consider Professional Help: If the infestation is severe or persists despite your efforts, contact a professional pest control service. Pest control professionals can assess the situation and recommend appropriate treatment measures.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about cockroach behavior and biology to better understand their habits and how to effectively manage their populations. Knowledge is a powerful tool in preventing and controlling cockroach infestations.
By taking these steps, you can effectively handle cockroach encounters and reduce the likelihood of future infestations, ensuring a safe and healthy living environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about cockroaches and their potential to live in the human body, along with their answers:
- Can cockroaches lay eggs inside the human body?
No, cockroaches cannot lay eggs inside the human body. Their preferred habitats are external environments with access to food and water. - What should I do if I find a cockroach in my home?
If you find a cockroach in your home, take preventive measures to eliminate potential food and water sources and seal entry points. Consider using traps and baits to control the population. - Are cockroaches dangerous to humans?
Cockroaches can pose health risks by spreading pathogens and triggering allergies, but they are not inherently dangerous. Effective pest control measures can mitigate these risks. - How do cockroaches enter homes?
Cockroaches can enter homes through cracks, crevices, and gaps around doors and windows. They may also hitch a ride on items brought into the home, such as groceries or luggage. - Can cockroaches survive without water?
Cockroaches require water to survive and can only go without it for about a week. They are more likely to persist in environments with accessible water sources. - Is it possible to completely eliminate cockroaches from a home?
While it may be challenging to completely eliminate cockroaches, effective pest control measures and preventive strategies can significantly reduce their populations and minimize encounters.
Conclusion
The question "can cockroaches live in your body" often sparks fear and curiosity, but the reality is that these resilient insects are unlikely to inhabit the human interior. While rare instances of accidental entry can occur, cockroaches are not biologically equipped to survive or thrive inside the human body.
Understanding the biology, behavior, and health risks associated with cockroaches is essential for effective pest control and prevention. By dispelling myths and focusing on science-based solutions, we can manage cockroach populations and protect our homes from infestations.
Ultimately, knowledge and vigilance are key to reducing the impact of cockroaches on our health and well-being. By implementing preventive measures and seeking professional assistance when needed, we can create a safe and healthy living environment free from these unwelcome pests.
Article Recommendations

