Understanding Cystic Acne: Causes, Treatments & Prevention Tips
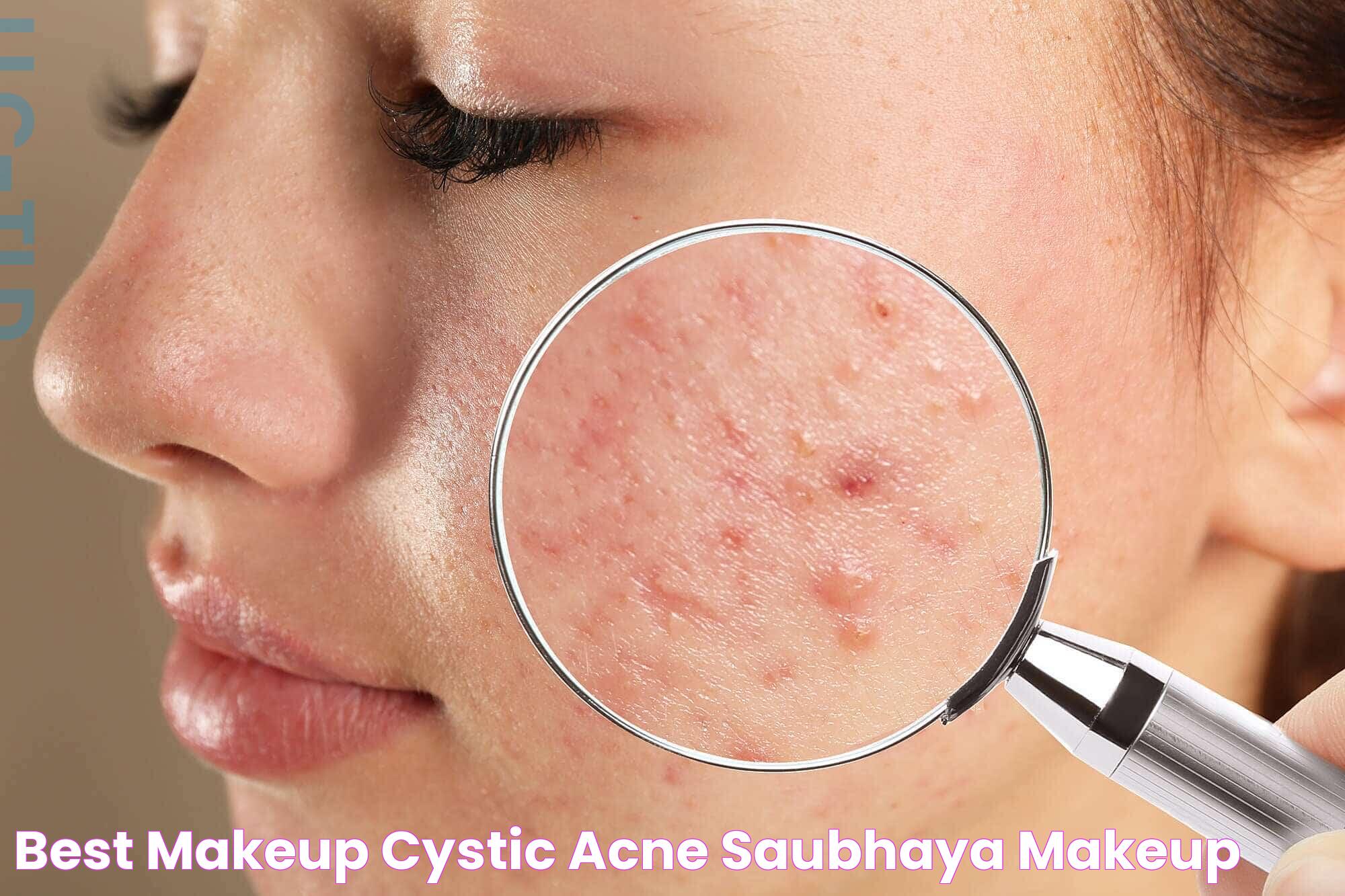
Cystic acne is more than just a troublesome skin condition; it's a severe form of acne that can significantly impact one's physical appearance and psychological well-being. This condition is characterized by large, painful cysts that form deep beneath the skin, often resulting in scarring if not treated appropriately. Unlike typical acne, which can be managed with over-the-counter treatments, cystic acne often requires medical intervention to effectively control and reduce symptoms.
For many individuals, cystic acne represents a frustrating cycle of flare-ups and temporary relief. It is most commonly seen in teenagers and young adults, but it can affect people of all ages. The deep-seated nature of the cysts makes them more challenging to treat than other forms of acne, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Anyone struggling with cystic acne should be aware of the various factors that contribute to its development and the most effective strategies for management.
Fortunately, advancements in dermatology have provided new insights into the treatment and prevention of cystic acne. By understanding the underlying causes and identifying effective treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and reduce the likelihood of future outbreaks. Whether you're seeking immediate relief or long-term solutions, this article will delve into every aspect of cystic acne, offering practical advice and expert recommendations to help you achieve clearer, healthier skin.
Read also:Top Tips And Insights About Best Buy Customer Service
Table of Contents
- What is Cystic Acne?
- Causes of Cystic Acne
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- How Does Cystic Acne Differ from Other Types of Acne?
- Treatment Options for Cystic Acne
- Are Home Remedies Effective for Cystic Acne?
- Medications for Managing Cystic Acne
- Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Cystic Acne
- Diet and Nutrition Tips
- When Should You See a Dermatologist?
- Psychological Impact of Cystic Acne
- Myths About Cystic Acne Debunked
- Future Trends in Cystic Acne Treatment
- FAQs About Cystic Acne
- Conclusion
What is Cystic Acne?
Cystic acne is a severe form of acne vulgaris, distinguished by the presence of large, painful cysts that develop beneath the skin's surface. These cysts are filled with pus and can cause significant discomfort and inflammation. Unlike milder forms of acne, cystic acne is more likely to lead to scarring due to the depth and severity of the lesions. Understanding cystic acne requires a grasp of its unique characteristics and the factors that contribute to its development.
Typically, cystic acne appears on the face, but it can also affect the chest, back, and shoulders. This condition is most prevalent in teenagers due to hormonal fluctuations during puberty, but adults can also experience it. The visibility and persistence of cystic acne often cause emotional distress and can impact one's self-esteem. Therefore, it's crucial to address both the physical and psychological aspects of this condition.
To effectively manage cystic acne, it's essential to understand its underlying causes, identify its symptoms, and seek appropriate treatment options. In the following sections, we will explore the various factors that lead to cystic acne, the symptoms that characterize this condition, and the most effective treatments available today.
Causes of Cystic Acne
The development of cystic acne is influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Understanding these causes is vital for effective treatment and prevention strategies. Here, we delve into the primary contributors to cystic acne:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly an increase in androgens, play a significant role in the onset of cystic acne. Androgens are male hormones present in both males and females, and an excess can lead to increased oil production in the skin. This excess oil, or sebum, can clog pores and create an environment conducive to bacteria growth, leading to inflammation and cyst formation.
2. Genetic Predisposition
Genetics can also influence one's likelihood of developing cystic acne. If close family members have experienced severe acne, there is a higher chance that you may also be predisposed to this condition. Genetic factors can affect skin sensitivity, oil production, and how the skin responds to hormonal changes.
Read also:Mastering Ice Hockey Rules Techniques And A Closer Look At The Sport
3. Bacterial Infection
The presence of certain bacteria, such as Propionibacterium acnes, on the skin can exacerbate cystic acne. These bacteria thrive in clogged pores and contribute to the inflammation and infection that characterize cystic acne. Controlling bacterial growth is a critical aspect of managing this condition.
4. Environmental Triggers
Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as pollution and humidity, can worsen cystic acne. These conditions can increase oil production and lead to clogged pores, making it more challenging to manage acne symptoms. It's essential to consider environmental influences when developing a skincare routine.
5. Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Stress is a known trigger for acne flare-ups, including cystic acne. When stressed, the body produces more cortisol, a hormone that can increase oil production and lead to acne formation. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as diet, sleep patterns, and skincare habits can impact the severity of cystic acne.
Understanding these causes can help individuals take targeted steps to reduce the risk and severity of cystic acne. In the following sections, we will explore the symptoms and diagnosis of cystic acne, as well as the most effective treatment options available today.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Cystic acne is characterized by distinct symptoms that differentiate it from other forms of acne. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Here, we outline the key features of cystic acne and the diagnostic process:
Common Symptoms of Cystic Acne
- Large, red, and painful cysts or nodules beneath the skin
- Swelling and inflammation around the affected area
- Persistent or recurring breakouts primarily on the face, chest, back, and shoulders
- Formation of pus-filled cysts that may rupture
- Scarring and discoloration following cyst healing
How is Cystic Acne Diagnosed?
Diagnosing cystic acne typically involves a thorough skin examination by a dermatologist. The dermatologist will assess the severity of the acne, the presence of cysts, and any scarring. In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to rule out other skin conditions or to identify underlying hormonal imbalances.
Dermatologists may also ask about family history, lifestyle factors, and any previous treatments attempted. This information helps in formulating a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of the individual.
If you suspect you have cystic acne, it's essential to seek professional advice to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In the next section, we will discuss how cystic acne differs from other types of acne and why this distinction matters in treatment approaches.
How Does Cystic Acne Differ from Other Types of Acne?
Cystic acne stands out from other forms of acne due to its severity, depth, and potential for scarring. Understanding these differences is crucial for determining the most effective treatment strategies. Here, we compare cystic acne with other common types of acne:
Cystic Acne vs. Common Acne
While common acne, also known as acne vulgaris, typically presents as blackheads, whiteheads, and small pimples, cystic acne involves deeper, pus-filled cysts. These cysts are more painful and inflamed than the typical acne lesions, and they are more likely to lead to scarring if not treated properly.
Cystic Acne vs. Nodular Acne
Nodular acne is similar to cystic acne in that it involves deep, painful lumps beneath the skin. However, nodular acne does not contain pus like cystic acne does. Both types of acne require medical treatment due to their severity and potential for scarring.
Why the Distinction Matters
Understanding the differences between cystic acne and other types of acne is essential for treatment planning. Cystic acne often requires more aggressive treatment approaches, including prescription medications and professional dermatological interventions. Over-the-counter treatments that work for milder acne may not be effective for cystic acne, underscoring the importance of seeking professional guidance.
In the next section, we will explore the various treatment options available for managing cystic acne, including both medical and home-based remedies. Understanding these options can help individuals make informed decisions about their skincare regimen.
Treatment Options for Cystic Acne
Effectively managing cystic acne requires a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Here, we outline the most common treatment options available to individuals seeking relief from this condition:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, such as retinoids and benzoyl peroxide, are often prescribed to help reduce inflammation and prevent new cysts from forming. These medications work by unclogging pores and reducing the presence of acne-causing bacteria on the skin.
2. Oral Medications
For more severe cases of cystic acne, oral medications may be necessary. Antibiotics, such as tetracycline or doxycycline, can reduce bacterial growth and inflammation. In some cases, oral contraceptives may be prescribed to help regulate hormones and reduce acne flare-ups in women.
3. Isotretinoin (Accutane)
Isotretinoin, commonly known as Accutane, is a powerful medication used to treat severe cystic acne. It works by shrinking the sebaceous glands, reducing oil production, and preventing clogged pores. Due to its potency and potential side effects, isotretinoin is typically reserved for cases that have not responded to other treatments.
4. Professional Procedures
Certain dermatological procedures can provide relief for cystic acne patients. These include chemical peels, laser therapy, and steroid injections, which can reduce inflammation and promote healing. These treatments are often used in conjunction with medications for optimal results.
In the next section, we will explore the effectiveness of home remedies for cystic acne and whether they can complement medical treatments.
Are Home Remedies Effective for Cystic Acne?
While medical treatments are often necessary for managing cystic acne, some individuals turn to home remedies as complementary options. Here, we examine the potential benefits and limitations of these remedies:
Popular Home Remedies for Cystic Acne
- Using tea tree oil for its antibacterial properties
- Applying aloe vera to soothe inflammation
- Employing honey and cinnamon masks for their antimicrobial effects
- Utilizing apple cider vinegar as a natural toner
- Applying green tea extract for its anti-inflammatory benefits
Limitations and Considerations
While these remedies may offer some relief for mild symptoms, they are unlikely to address the underlying causes of cystic acne. It's essential to use home remedies in conjunction with medical treatments and under the guidance of a dermatologist. Some natural products may cause irritation or allergic reactions, so it's crucial to test them on a small area of skin first.
In the next section, we will delve into the medications commonly prescribed for managing cystic acne and their effectiveness.
Medications for Managing Cystic Acne
Medications are a cornerstone of cystic acne treatment, helping to control inflammation, reduce bacterial growth, and prevent new cysts from forming. Here, we explore the most commonly prescribed medications for managing this condition:
1. Topical Retinoids
Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin and adapalene, are derived from vitamin A and work by promoting cell turnover and preventing clogged pores. They are effective in reducing the formation of new cysts and are often used in combination with other treatments.
2. Antibiotics
Oral and topical antibiotics are prescribed to reduce the presence of acne-causing bacteria and inflammation. Common options include clindamycin, erythromycin, and doxycycline. These medications are typically used for a short duration to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
3. Hormonal Therapies
For women, hormonal therapies, such as oral contraceptives and spironolactone, can help regulate hormones and reduce acne flare-ups. These medications are particularly effective for individuals whose acne is linked to hormonal imbalances.
4. Isotretinoin (Accutane)
As mentioned earlier, isotretinoin is a potent medication reserved for severe cystic acne cases. It is highly effective but requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects, including dry skin, birth defects, and changes in mood.
In the next section, we will discuss lifestyle changes that can help prevent cystic acne and support overall skin health.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Cystic Acne
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle adjustments can help prevent cystic acne and promote healthier skin. Here, we outline several strategies individuals can implement:
1. Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine
A consistent skincare routine is essential for managing cystic acne. This includes cleansing the skin twice daily with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser, applying topical treatments as prescribed, and using a moisturizer to maintain skin hydration.
2. Avoid Picking or Squeezing Cysts
Picking or squeezing cysts can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring. It's crucial to resist the temptation to touch affected areas and to seek professional treatment for severe breakouts.
3. Manage Stress Levels
Since stress is a known trigger for acne, finding ways to manage stress can help prevent flare-ups. This may include practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
4. Get Adequate Sleep
Getting enough sleep is vital for maintaining overall health and skin wellness. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support the body's natural healing processes.
In the next section, we will explore the role of diet and nutrition in managing cystic acne and offer practical tips for making healthier choices.
Diet and Nutrition Tips
Diet and nutrition can play a significant role in the management of cystic acne. While no specific diet can cure acne, certain dietary changes may help reduce symptoms and promote clearer skin. Here, we offer practical tips for incorporating skin-friendly foods into your diet:
1. Focus on Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids), leafy greens, berries, and nuts, can help reduce inflammation and support skin health.
2. Limit Dairy and High-Glycemic Foods
Research suggests that dairy products and high-glycemic foods, such as white bread, sugary snacks, and processed foods, may contribute to acne flare-ups. Consider reducing your intake of these foods and opting for whole grains, lean proteins, and fresh produce instead.
3. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for skin hydration and detoxification. Aim to consume at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily to support your body's natural processes.
4. Consider Probiotics
Probiotics, found in foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, can support gut health and may have a positive impact on skin conditions. Incorporating probiotics into your diet may help balance the skin's microbiome and reduce acne symptoms.
In the next section, we will discuss when it's appropriate to seek the advice of a dermatologist for cystic acne treatment.
When Should You See a Dermatologist?
While mild cases of acne can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments, cystic acne typically requires medical intervention. Here, we outline when it's appropriate to seek the advice of a dermatologist:
Signs You Should Consult a Dermatologist
- Persistent or worsening cystic acne despite using over-the-counter products
- Severe pain or discomfort associated with cysts
- Significant scarring or discoloration from previous cysts
- Emotional distress or low self-esteem due to acne
- Desire for professional treatment options, such as prescription medications or procedures
What to Expect During a Dermatology Appointment
During a dermatology appointment, the dermatologist will assess your skin condition, discuss your medical history, and recommend a personalized treatment plan. This plan may include prescription medications, lifestyle recommendations, and follow-up appointments to monitor progress.
Seeking professional advice ensures that you receive the most effective treatment for your specific needs and reduces the risk of long-term scarring or complications.
In the next section, we will explore the psychological impact of cystic acne and strategies for coping with its effects.
Psychological Impact of Cystic Acne
Cystic acne can have a significant psychological impact, affecting self-esteem, social interactions, and overall quality of life. Here, we explore the emotional challenges associated with cystic acne and offer strategies for coping:
Emotional Effects of Cystic Acne
- Feelings of embarrassment or self-consciousness about appearance
- Withdrawal from social activities or avoidance of public settings
- Anxiety or depression related to acne severity
- Frustration or hopelessness about treatment outcomes
Coping Strategies
- Seek support from friends, family, or support groups who understand your experiences
- Practice positive self-talk and focus on your strengths and accomplishments
- Engage in activities that boost your confidence and self-esteem
- Consult a mental health professional for guidance if experiencing significant emotional distress
Understanding the psychological impact of cystic acne is essential for developing a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both physical and emotional well-being.
In the next section, we will debunk common myths about cystic acne and provide accurate information to help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment.
Myths About Cystic Acne Debunked
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding cystic acne that can lead to ineffective treatment approaches. Here, we debunk some of the most common myths to provide accurate information:
Myth #1: Acne is Caused by Poor Hygiene
Fact: While maintaining a proper skincare routine is important, acne is not caused by poor hygiene. Cystic acne is primarily influenced by hormonal, genetic, and environmental factors.
Myth #2: Sun Exposure Clears Acne
Fact: Although sunlight may temporarily reduce acne inflammation, excessive sun exposure can worsen acne by increasing oil production and causing skin damage.
Myth #3: Only Teenagers Get Acne
Fact: While acne is common during adolescence, adults of all ages can develop cystic acne due to hormonal changes, stress, or other factors.
Myth #4: Popping Cysts Speeds Up Healing
Fact: Popping cysts can lead to increased inflammation, infection, and scarring. It's best to leave cysts alone and seek professional treatment.
By debunking these myths, individuals can make informed decisions about their acne treatment and avoid common pitfalls.
In the next section, we will explore future trends in cystic acne treatment and the potential for new advancements in this field.
Future Trends in Cystic Acne Treatment
The field of dermatology is continually evolving, with new research and technologies offering promising advancements in cystic acne treatment. Here, we explore potential future trends that may revolutionize how this condition is managed:
1. Personalized Medicine
Advancements in genetic research and personalized medicine may lead to more tailored treatment plans based on an individual's unique genetic makeup. This approach could improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of side effects.
2. Advanced Laser and Light Therapies
Innovative laser and light-based therapies, such as blue light and photodynamic therapy, are being developed to target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation more effectively.
3. Microbiome-Based Treatments
Research into the skin's microbiome is uncovering new insights into acne management. Future treatments may focus on balancing the skin's microbiome to reduce acne symptoms and promote healthier skin.
4. Novel Topical and Oral Medications
Scientists are exploring new compounds and drug formulations that may offer more effective and safer options for cystic acne treatment. These advancements could provide alternative solutions for individuals who do not respond to current therapies.
As research continues, these trends hold the potential to improve the quality of life for individuals with cystic acne and offer new hope for effective management.
FAQs About Cystic Acne
1. Can cystic acne go away on its own?
While mild acne may resolve on its own, cystic acne typically requires medical treatment to prevent scarring and manage symptoms effectively.
2. What is the best treatment for cystic acne scars?
Treatment options for cystic acne scars include chemical peels, laser therapy, and microneedling. It's essential to consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
3. Are there any natural remedies for cystic acne?
Natural remedies, such as tea tree oil and aloe vera, may offer some relief for mild symptoms, but they should be used alongside medical treatments for best results.
4. How long does it take for cystic acne to heal?
The healing time for cystic acne varies depending on the severity and treatment approach. With proper medical intervention, improvement can be seen within a few weeks to months.
5. Can diet affect cystic acne?
Diet can play a role in acne management. Reducing dairy and high-glycemic foods may help reduce symptoms, while incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can support skin health.
6. Is cystic acne hereditary?
Cystic acne can have a genetic component, meaning individuals with a family history of severe acne may be more prone to developing the condition.
Conclusion
Cystic acne is a challenging condition that requires a comprehensive approach for effective management. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to achieve clearer, healthier skin. Whether through medical intervention, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both, there are numerous strategies available to reduce the impact of cystic acne and improve overall well-being.
With ongoing advancements in dermatology, there is hope for even more effective treatments in the future. For those struggling with cystic acne, seeking professional guidance and support is essential for achieving the best possible outcomes.
Article Recommendations

