Enhancing Security: The Power Of Multifactor Authentication
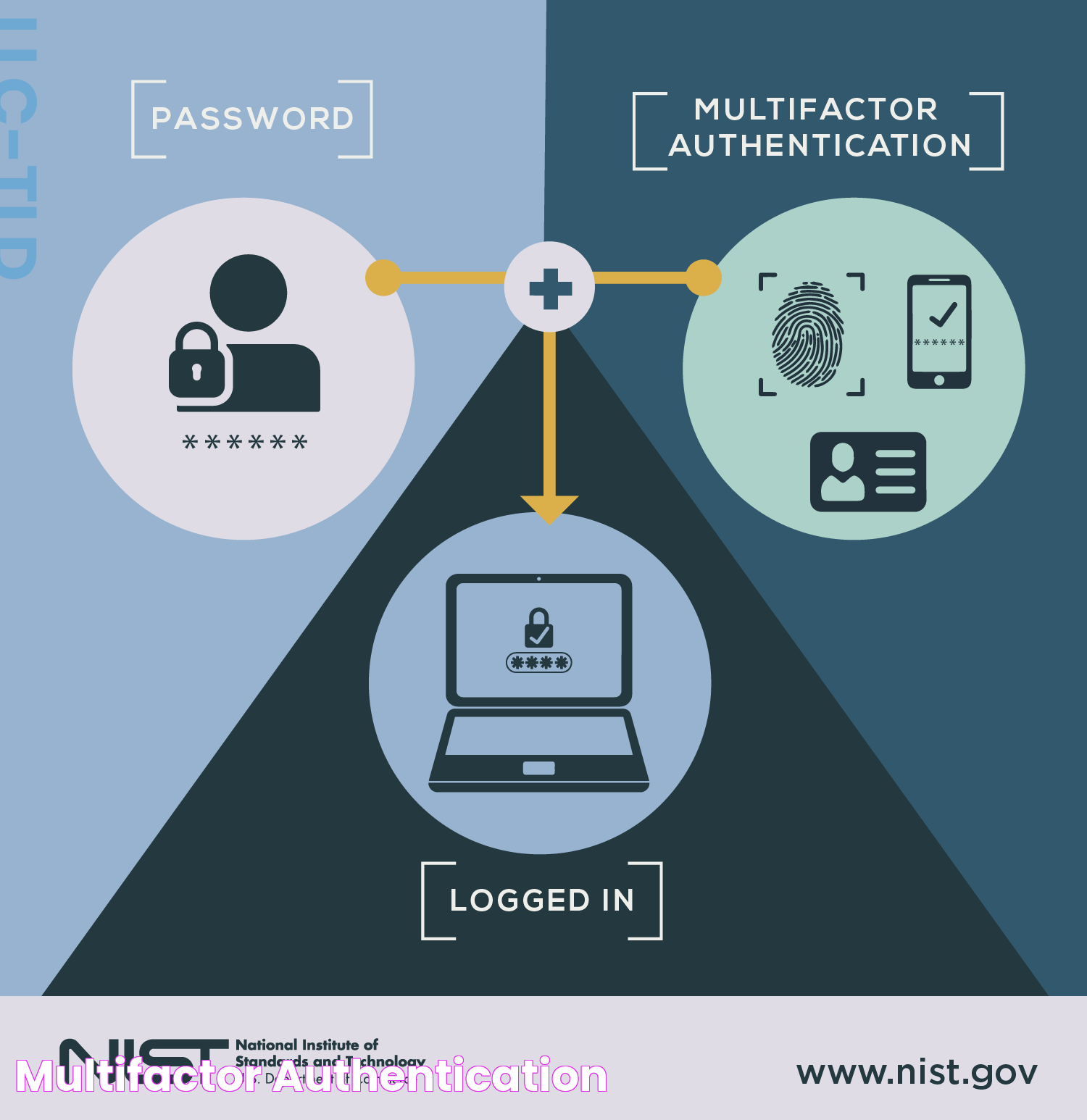
In today's digital landscape, multifactor authentication (MFA) has emerged as a vital tool for safeguarding sensitive information and protecting user accounts. As cyber threats continue to evolve, relying solely on traditional username and password combinations is no longer sufficient. MFA offers an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to their accounts. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and enhances overall security measures.
Multifactor authentication operates on the principle of using two or more independent credentials from three distinct categories: something the user knows (such as a password), something the user has (such as a smartphone or security token), and something the user is (such as biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition). By combining these factors, MFA ensures that even if one element is compromised, the likelihood of unauthorized access remains minimal. This layered approach has proven to be highly effective in mitigating cyber threats and protecting sensitive data.
The adoption of multifactor authentication is becoming increasingly widespread across various industries, from healthcare and finance to education and government sectors. Organizations are recognizing the importance of implementing MFA to safeguard their systems and protect their users' data. As technology continues to advance, MFA is evolving to incorporate new methods and technologies, making it an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of multifactor authentication, its benefits, implementation strategies, and future trends in this rapidly evolving field.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Football Teams History Rivalries And Impact
Table of Contents
- What is Multifactor Authentication?
- Why is MFA Important?
- How Does MFA Work?
- Types of Authentication Factors
- Implementing MFA in Businesses
- Benefits of Multifactor Authentication
- Challenges and Limitations of MFA
- How to Overcome MFA Challenges?
- Future of Multifactor Authentication
- MFA and User Experience
- Common MFA Methods
- MFA in Different Industries
- How to Choose the Right MFA Solution?
- FAQs about Multifactor Authentication
- Conclusion
What is Multifactor Authentication?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify a user's identity. The goal of MFA is to create a layered defense that makes it more difficult for an unauthorized person to access a target, such as a physical location, computing device, network, or database.
The concept of multifactor authentication is not new. Historically, it has been used in various forms, such as requiring a key and a code to open a safe. In the digital world, MFA has become increasingly important as cyber threats and data breaches have become more prevalent. By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA provides an extra layer of security beyond just a username and password.
MFA is designed to protect both the user and the organization from potential security breaches. By implementing MFA, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems. This added security measure is particularly important for industries that handle sensitive data, such as healthcare and finance.
Why is MFA Important?
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are on the rise, multifactor authentication has emerged as a critical component of any robust security strategy. Here's why MFA is important:
- Enhanced Security: By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Protection Against Phishing: Even if a user's password is compromised, MFA provides an additional barrier that prevents unauthorized access.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have regulatory requirements that mandate the use of MFA to protect sensitive data.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: With MFA, the risk of data breaches is minimized, protecting both the organization and its users.
- Building User Trust: Implementing MFA demonstrates a commitment to security, helping to build trust with users and customers.
In summary, MFA is a powerful tool that enhances security, protects against phishing, ensures compliance with regulations, reduces the risk of data breaches, and builds user trust. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of MFA will only continue to grow.
How Does MFA Work?
Multifactor authentication works by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource such as an application, online account, or VPN. MFA is based on the premise that multiple layers of authentication provide better security than a single factor alone.
Read also:Discover The Best Learning Platforms For Enhanced Education
The process of MFA typically involves the following steps:
- User Login: The user attempts to log in to a system or application using their username and password.
- First Factor Authentication: The system verifies the user's credentials (username and password) as the first factor of authentication.
- Second Factor Authentication: The system prompts the user to provide a second form of verification, such as a one-time code sent to their phone or a fingerprint scan.
- Access Granted: Once the system verifies both factors, the user is granted access to the system or application.
MFA can incorporate a variety of factors, including:
- Knowledge Factors: Something the user knows, such as a password or PIN.
- Possession Factors: Something the user has, such as a security token or smartphone.
- Inherence Factors: Something the user is, such as biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition.
By combining these factors, MFA provides a higher level of security than traditional authentication methods, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
Types of Authentication Factors
Multifactor authentication relies on the use of multiple authentication factors to verify a user's identity. These factors can be categorized into three main types:
What are Knowledge Factors?
Knowledge factors are something the user knows, such as:
- Passwords: A secret combination of letters, numbers, and symbols used to authenticate a user.
- PINs: A personal identification number used for verification.
- Security Questions: Questions that only the user should know the answer to, used for additional verification.
Knowledge factors are the most common form of authentication but are also the most vulnerable to attacks such as phishing and social engineering.
What are Possession Factors?
Possession factors are something the user has, such as:
- Security Tokens: Physical devices that generate a one-time code for authentication.
- Smartphones: Devices that can receive one-time codes via SMS or app-based authenticator.
- Smart Cards: Cards with embedded chips used for authentication.
Possession factors add an additional layer of security, as they require the user to have a physical item in their possession.
What are Inherence Factors?
Inherence factors are something the user is, such as:
- Biometric Data: Unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
- Voice Recognition: The use of voice patterns for authentication.
Inherence factors offer a high level of security as they are unique to each individual and difficult to replicate.
By combining these authentication factors, MFA provides a robust security framework that is difficult for attackers to bypass.
Implementing MFA in Businesses
Implementing multifactor authentication in businesses is a crucial step in enhancing the security of organizational systems and data. Here are key considerations for businesses looking to implement MFA:
Assessing Security Needs
Before implementing MFA, businesses should conduct a thorough assessment of their security needs. This includes identifying sensitive data, understanding potential threats, and evaluating existing security measures. By understanding these factors, businesses can determine the most appropriate MFA solution for their needs.
Choosing the Right MFA Solution
There are various MFA solutions available in the market, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Businesses should consider factors such as ease of use, integration with existing systems, and cost when choosing an MFA solution. Additionally, businesses should ensure that the chosen solution aligns with their security needs and regulatory requirements.
Implementing MFA for All Users
Once a suitable MFA solution has been selected, businesses should implement it for all users, including employees, contractors, and third-party vendors. This ensures that all access points are protected and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Providing User Training and Support
Implementing MFA may require users to change their login habits, so it's important to provide training and support to help them adapt. This includes educating users on the benefits of MFA, how to use it, and what to do if they encounter any issues.
By following these steps, businesses can successfully implement MFA and enhance their overall security posture.
Benefits of Multifactor Authentication
Multifactor authentication offers numerous benefits that enhance security and protect organizations from potential threats. Here are some key benefits of MFA:
- Increased Security: By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Protection Against Phishing: MFA provides an additional layer of security that protects against phishing attacks, even if a user's password is compromised.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have regulatory requirements that mandate the use of MFA to protect sensitive data.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: With MFA, the risk of data breaches is minimized, protecting both the organization and its users.
- Improved User Trust: Implementing MFA demonstrates a commitment to security, helping to build trust with users and customers.
- Flexibility and Scalability: MFA solutions can be tailored to meet the specific needs of an organization, providing flexibility and scalability as the organization grows.
Overall, MFA is a powerful tool that enhances security, protects against phishing, ensures compliance with regulations, reduces the risk of data breaches, and builds user trust. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of MFA will only continue to grow.
Challenges and Limitations of MFA
While multifactor authentication offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges and limitations that organizations must consider. Here are some common challenges associated with MFA:
What are the Technical Challenges?
Implementing MFA can present technical challenges, such as:
- Integration with Existing Systems: MFA solutions may need to be integrated with existing systems and applications, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Compatibility Issues: Some MFA solutions may not be compatible with certain devices or software, limiting their effectiveness.
- Network Connectivity: MFA often relies on network connectivity to function, which can be an issue in areas with poor internet access.
These technical challenges can impact the effectiveness of MFA and may require additional resources to address.
What are the User Challenges?
Users may also face challenges when using MFA, such as:
- Usability and Convenience: MFA can add an extra step to the login process, which some users may find inconvenient or cumbersome.
- User Resistance: Users may be resistant to change and may not fully understand the benefits of MFA, leading to reluctance in adoption.
- Lost or Forgotten Devices: If a user loses their device used for MFA, it can result in access issues and delays.
Addressing these user challenges requires effective communication and training to ensure a smooth transition to MFA.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of MFA far outweigh the limitations, making it a critical component of any organization's security strategy.
How to Overcome MFA Challenges?
While multifactor authentication presents certain challenges, organizations can take steps to overcome these obstacles and ensure a successful implementation. Here's how to address common MFA challenges:
Addressing Technical Challenges
To overcome technical challenges, organizations can:
- Choose Compatible Solutions: Select MFA solutions that are compatible with existing systems and devices to minimize integration issues.
- Leverage Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based MFA solutions can reduce the complexity of on-premises deployments and offer greater flexibility.
- Ensure Redundancy: Implement redundancy measures to address network connectivity issues and ensure continuous access.
Enhancing User Experience
To improve user experience and address user challenges, organizations can:
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Educate users on the benefits of MFA and provide training on how to use it effectively.
- Offer Multiple Authentication Options: Provide users with a variety of authentication options to choose from, such as biometrics or app-based authenticators.
- Streamline the Login Process: Implement measures to streamline the MFA login process, reducing inconvenience for users.
By addressing these challenges, organizations can maximize the effectiveness of MFA and enhance their overall security strategy.
Future of Multifactor Authentication
The future of multifactor authentication is marked by innovation and adaptation to emerging technologies and evolving cyber threats. As organizations continue to prioritize security, MFA is poised to play a critical role in safeguarding data and systems. Here are some key trends and developments shaping the future of MFA:
Advancements in Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication is gaining traction as a secure and convenient method of verification. Future developments in biometrics may include more advanced facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition technologies. These advancements will enhance the accuracy and reliability of biometric factors, making them a preferred choice for MFA.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to play a significant role in the future of MFA. AI algorithms can analyze user behavior patterns and detect anomalies, providing an additional layer of security. This integration can help identify and prevent potential security threats in real-time, further enhancing the effectiveness of MFA.
Expansion of Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication is gaining momentum as organizations seek to eliminate the vulnerabilities associated with traditional passwords. Future MFA solutions may prioritize passwordless methods, such as biometric authentication or hardware tokens, to provide a seamless and secure user experience.
Focus on User Experience
As MFA continues to evolve, there will be a greater emphasis on improving user experience. Future solutions will aim to strike a balance between security and convenience, offering users a frictionless authentication process without compromising security.
Overall, the future of multifactor authentication is bright, with continuous advancements in technology and a growing focus on enhancing security and user experience. As cyber threats persist, MFA will remain a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity strategies.
MFA and User Experience
Multifactor authentication plays a vital role in enhancing security, but it also impacts user experience. Striking the right balance between security and convenience is crucial to ensure that users embrace MFA without facing unnecessary friction. Here's how MFA influences user experience and how organizations can optimize it:
Impact on User Experience
MFA can influence user experience in several ways:
- Increased Security: Users appreciate the added security that MFA provides, giving them confidence that their accounts and data are protected.
- Extra Step in Login Process: MFA introduces an additional step in the login process, which may be perceived as inconvenient by some users.
- Potential for Frustration: Users may feel frustrated if they encounter issues with MFA, such as lost devices or difficulty accessing authentication codes.
Optimizing User Experience
To enhance user experience while maintaining security, organizations can implement the following strategies:
- Offer Multiple Authentication Options: Provide users with a variety of authentication methods, such as biometrics, app-based authentication, or hardware tokens, to choose from based on their preferences and convenience.
- Streamline the Authentication Process: Implement measures to streamline the MFA login process, such as reducing the number of steps required or integrating MFA with single sign-on solutions.
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly communicate the benefits of MFA to users, emphasizing the importance of security and how it protects their accounts and data.
- Provide Support and Assistance: Offer user support and assistance to address any issues or concerns related to MFA, ensuring a positive user experience.
By focusing on user experience, organizations can encourage user adoption of MFA while maintaining a strong security posture. This balance is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of multifactor authentication.
Common MFA Methods
Multifactor authentication employs various methods to verify a user's identity, each offering a unique approach to enhancing security. Here are some common MFA methods used by organizations:
One-Time Passwords (OTPs)
One-time passwords are temporary codes generated for a single login session or transaction. OTPs can be delivered via SMS, email, or app-based authenticator. They provide an additional layer of security by requiring users to enter a unique code in addition to their password.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication uses unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, to verify a user's identity. Biometrics offer a high level of security and convenience, as they are difficult to replicate and do not require users to remember additional credentials.
Hardware Tokens
Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate a one-time code for authentication. Users must have the token in their possession to access their accounts, adding an extra layer of security. Hardware tokens are often used in high-security environments where additional protection is required.
App-Based Authentication
App-based authentication involves the use of mobile apps, such as Google Authenticator or Authy, to generate one-time codes for verification. These apps provide a convenient and secure method of authentication, as they do not rely on network connectivity for code generation.
Each of these MFA methods offers unique advantages and can be tailored to meet the specific security needs of an organization. By incorporating multiple methods, organizations can create a robust and effective multifactor authentication system.
MFA in Different Industries
Multifactor authentication is widely adopted across various industries to enhance security and protect sensitive data. Here are some examples of how MFA is implemented in different sectors:
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, MFA is used to protect patient data and ensure compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Healthcare organizations implement MFA to secure access to electronic health records, prescription management systems, and other critical applications.
Finance
The finance sector relies heavily on MFA to safeguard financial transactions and protect customer data. Banks and financial institutions use MFA to secure online banking, mobile applications, and payment systems. MFA helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of fraud.
Education
Educational institutions implement MFA to protect student and faculty data, as well as to secure access to online learning platforms and administrative systems. MFA helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information and ensures a safe and secure learning environment.
Government
Government agencies use MFA to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with security regulations. MFA is implemented to secure access to government networks, databases, and applications, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Each industry has unique security requirements, and MFA can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each sector. By implementing MFA, organizations across various industries can enhance their security posture and protect sensitive data.
How to Choose the Right MFA Solution?
Selecting the right multifactor authentication solution is crucial for enhancing security and protecting sensitive data. Here are key considerations for choosing the right MFA solution:
Assessing Security Requirements
Organizations should begin by assessing their security requirements and understanding the specific threats they face. This includes identifying sensitive data, evaluating existing security measures, and determining the level of protection needed. By understanding these factors, organizations can choose an MFA solution that aligns with their security needs.
Evaluating Compatibility and Integration
It's important to choose an MFA solution that is compatible with existing systems and applications. Organizations should evaluate the solution's integration capabilities and ensure that it can be seamlessly integrated into their existing infrastructure. Compatibility with various devices and platforms is also a key consideration.
Considering User Experience
Organizations should prioritize user experience when selecting an MFA solution. The solution should offer a convenient and seamless authentication process, with minimal disruption to users. Providing multiple authentication options can enhance user experience and encourage adoption.
Reviewing Cost and Scalability
Cost is an important factor when choosing an MFA solution. Organizations should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including implementation, maintenance, and licensing fees. Scalability is also crucial, as the solution should be able to accommodate future growth and evolving security needs.
By considering these factors, organizations can choose the right MFA solution that enhances security, meets their specific requirements, and provides a positive user experience.
FAQs about Multifactor Authentication
What is multifactor authentication?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify a user's identity. It provides an additional layer of security beyond just a username and password.
Why is multifactor authentication important?
MFA is important because it enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, and protecting sensitive data. It also helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and build user trust.
What types of authentication factors are used in MFA?
MFA uses multiple authentication factors, including knowledge factors (something the user knows), possession factors (something the user has), and inherence factors (something the user is, such as biometric data).
How does multifactor authentication work?
MFA works by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors, such as a password and a one-time code, to gain access to a resource. This layered approach provides better security than a single factor alone.
What are common methods of multifactor authentication?
Common MFA methods include one-time passwords (OTPs), biometric authentication (fingerprints, facial recognition), hardware tokens, and app-based authentication (such as Google Authenticator).
How can organizations choose the right MFA solution?
Organizations can choose the right MFA solution by assessing their security requirements, evaluating compatibility and integration capabilities, considering user experience, and reviewing cost and scalability. These factors help ensure the solution meets their specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multifactor authentication is a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies. By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA provides an additional layer of security that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of MFA will only continue to grow.
MFA offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security, protection against phishing, compliance with regulations, reduced risk of data breaches, and improved user trust. Despite certain challenges, such as technical and user-related issues, organizations can overcome these obstacles by implementing the right strategies and solutions.
As the future of multifactor authentication unfolds, advancements in technology, such as biometric authentication and artificial intelligence, will further enhance its effectiveness and user experience. By adopting MFA, organizations can safeguard their systems, protect sensitive data, and build a secure digital environment for users and customers alike.
Article Recommendations

