Game Theory: Strategies, Applications, And Real-World Impact
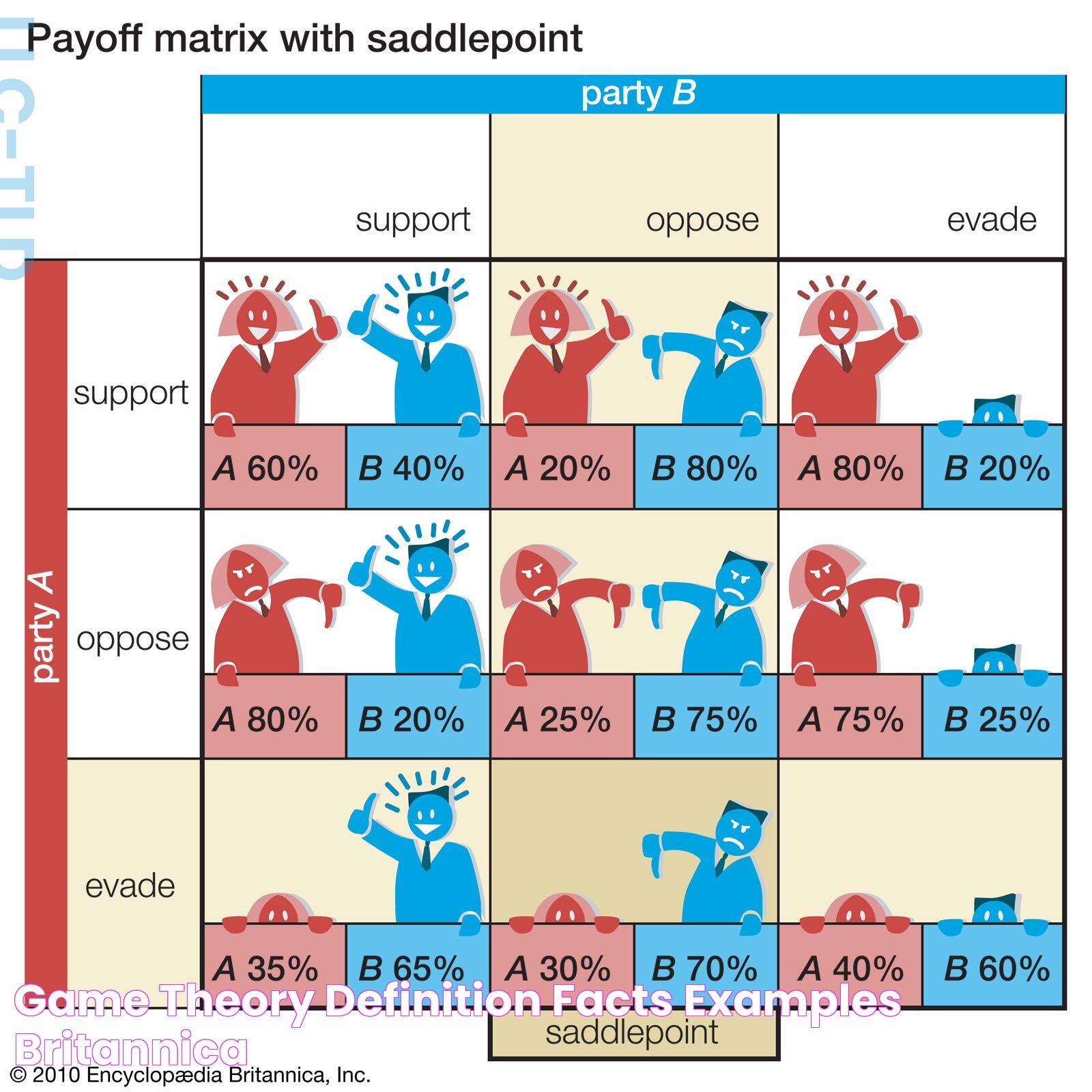
Game theory is a fascinating branch of mathematics and economics that explores strategic interactions where the outcome for each participant depends on the actions of others. It provides a framework for understanding how individuals, businesses, and even nations make decisions in competitive situations. At its core, game theory seeks to identify the best strategies for players in scenarios ranging from board games to complex economic markets. This analytical approach has revolutionized our understanding of competitive behavior, allowing us to predict and influence outcomes in various fields.
In recent years, game theory has gained significant popularity, not just among academics but also in popular culture and business strategy. Its concepts are widely applied in economics, political science, psychology, and evolutionary biology, among others. Game theory helps us recognize the strategic nature of interactions and the potential for cooperation or conflict, offering insights into human behavior and decision-making processes. With its growing relevance, understanding game theory has become essential for anyone looking to navigate competitive environments successfully.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deep into the world of game theory. We'll explore its foundational principles, key concepts, and diverse applications in real-world scenarios. From simple games like the prisoner's dilemma to complex economic models, game theory provides a unique lens through which we can view and interpret a wide array of strategic interactions. So, whether you're a student, a professional, or simply curious about the intricacies of decision-making, this article is your gateway to mastering game theory.
Read also:Patricia Arkette The Multifaceted Persona And Her Unforgettable Impact
Table of Contents
- Foundations of Game Theory
- Key Concepts in Game Theory
- Types of Games in Game Theory
- Real-World Applications of Game Theory
- Game Theory in Economics
- Political Strategy and Game Theory
- Evolutionary Biology and Game Theory
- How Does Game Theory Influence Technology?
- Game Theory in Business and Marketing
- Can Game Theory Predict Human Behavior?
- Ethical Implications of Game Theory
- Common Misconceptions About Game Theory
- What Are the Limitations of Game Theory?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Foundations of Game Theory
Game theory is a mathematical framework that seeks to understand and analyze competitive situations where the outcome depends on the actions of multiple decision-makers or "players." These players can be individuals, companies, or even countries. The field was developed in the mid-20th century, with John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern’s groundbreaking work, "Theory of Games and Economic Behavior," which laid the foundation for modern game theory.
The essence of game theory lies in the concept of strategic interaction. It assumes that each player is rational and aims to maximize their payoff or benefit, given the strategies of other players. This creates a complex web of interdependent decisions, where the success of one player is contingent on the choices made by others.
Game theory relies on several key assumptions:
- Rationality: Players are rational and seek to maximize their utility or payoff.
- Common Knowledge: All players are aware of the game's rules and the rationality of other players.
- Strategic Interdependence: The outcome for each player depends on the choices of others.
These assumptions form the basis for analyzing different types of games and strategic scenarios.
Key Concepts in Game Theory
What is a Strategy?
In game theory, a strategy refers to a comprehensive plan that outlines a player's actions in every possible situation within a game. It is a predetermined course of action that a player follows to achieve the best possible outcome. Strategies can be simple or complex, depending on the nature of the game and the number of players involved.
There are two primary types of strategies:
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Bristol Motor Speedway History Events And More
- Pure Strategy: A strategy where a player consistently chooses a specific action in every scenario.
- Mixed Strategy: A strategy in which a player randomizes their actions to achieve the best possible outcome.
The choice between pure and mixed strategies depends on the game's structure and the player's objectives.
Nash Equilibrium and Its Significance
The Nash Equilibrium is a central concept in game theory, named after mathematician John Nash. It represents a stable state in a game where no player can benefit by changing their strategy while the other players' strategies remain unchanged. At this point, each player's strategy is the best response to the strategies of others.
The Nash Equilibrium is significant because it helps predict the outcome of strategic interactions. It indicates that rational players are unlikely to deviate from their chosen strategies, as doing so would not improve their payoff. This concept has practical applications in various fields, including economics, politics, and evolutionary biology.
Types of Games in Game Theory
Cooperative vs. Non-Cooperative Games
Game theory distinguishes between two main types of games: cooperative and non-cooperative. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing strategic interactions.
Cooperative Games: In cooperative games, players can form alliances or coalitions to achieve a common goal. Cooperation is explicitly allowed, and players work together to maximize their collective payoff. These games often involve binding agreements and shared strategies.
Non-Cooperative Games: In non-cooperative games, players act independently and cannot form binding agreements. Each player pursues their interests, leading to competition and potentially conflicting strategies. Non-cooperative games focus on individual decision-making and strategic interactions.
Zero-Sum and Non-Zero-Sum Games
Another important distinction in game theory is between zero-sum and non-zero-sum games, which describe the distribution of payoffs among players.
Zero-Sum Games: In zero-sum games, one player's gain is exactly equal to the loss of another player. The total payoff remains constant, meaning that the sum of all players' payoffs is zero. These games often involve direct competition, such as chess or poker, where one player's victory results in another's defeat.
Non-Zero-Sum Games: In non-zero-sum games, the total payoff can vary, allowing for potential cooperation and mutual benefit. Players can achieve positive outcomes without undermining others. These games reflect real-world scenarios where collaboration and negotiation can lead to better results for all involved.
Real-World Applications of Game Theory
Game theory has a wide range of applications across various fields, offering valuable insights into strategic decision-making. From economics to biology, its principles are used to analyze and predict outcomes in numerous real-world situations.
Some notable applications of game theory include:
- Economics: Game theory helps economists understand market dynamics, pricing strategies, and competitive behavior among firms.
- Political Science: Game theory is used to analyze voting behavior, coalition formation, and international relations.
- Biology: Evolutionary game theory explores how species adapt and evolve through strategic interactions.
- Business: Companies use game theory to develop competitive strategies, negotiate contracts, and optimize supply chains.
- Technology: Game theory informs the design of algorithms, network protocols, and cybersecurity strategies.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and relevance of game theory in understanding complex interactions and making informed decisions.
Game Theory in Economics
In economics, game theory provides a powerful tool for analyzing market behavior and competitive interactions among firms. It helps economists understand how businesses strategize to maximize profits and gain a competitive edge. Game theory is particularly relevant in oligopolistic markets, where a few dominant firms influence prices and market conditions.
Key economic applications of game theory include:
- Pricing Strategies: Firms use game theory to determine optimal pricing strategies, considering the potential reactions of competitors.
- Market Entry and Exit: Game theory helps analyze the strategic decisions of firms entering or exiting a market.
- Auctions: Game theory informs the design and analysis of auction mechanisms, ensuring fair and efficient outcomes.
- Bargaining and Negotiation: Game theory models bargaining scenarios, helping parties reach mutually beneficial agreements.
By understanding these economic applications, businesses can make more informed decisions and navigate competitive markets more effectively.
Political Strategy and Game Theory
Game theory plays a crucial role in political science, offering insights into the strategic behavior of political actors and the dynamics of international relations. It helps analyze voting behavior, coalition formation, and decision-making processes in political systems.
Some political applications of game theory include:
- Voting Systems: Game theory models voting behavior, helping to understand how different electoral systems influence outcomes.
- Coalition Formation: Game theory analyzes the formation of political alliances and coalitions to achieve shared goals.
- International Relations: Game theory helps analyze strategic interactions between countries, including diplomacy and conflict resolution.
- Policy Design: Game theory informs the design of policies and regulations, considering the potential responses of stakeholders.
By applying game theory to political strategies, policymakers can make more informed decisions and navigate complex political landscapes effectively.
Evolutionary Biology and Game Theory
In evolutionary biology, game theory provides a framework for understanding how organisms adapt and evolve through strategic interactions. Evolutionary game theory explores the dynamics of cooperation, competition, and survival in natural systems.
Some key concepts in evolutionary game theory include:
- Evolutionarily Stable Strategies (ESS): Strategies that persist over generations because they offer a competitive advantage.
- Altruism and Cooperation: Game theory models explain how cooperative behaviors can evolve and persist in populations.
- Competition and Conflict: Game theory analyzes the strategic interactions that drive competition and conflict among species.
By applying game theory to evolutionary biology, researchers can gain insights into the complex dynamics of natural selection and adaptation.
How Does Game Theory Influence Technology?
Game theory has a significant impact on technology, informing the design and development of algorithms, network protocols, and cybersecurity strategies. It provides a framework for understanding the strategic interactions between different technological components and user behaviors.
Some technological applications of game theory include:
- Algorithm Design: Game theory helps optimize algorithms for efficiency and fairness in resource allocation.
- Network Protocols: Game theory models inform the design of communication protocols, ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission.
- Cybersecurity: Game theory analyzes strategic interactions between attackers and defenders, enhancing security measures.
- Artificial Intelligence: Game theory informs the development of AI systems that can navigate strategic interactions with humans and other AI agents.
By leveraging game theory in technology, developers can create more robust and efficient systems that optimize performance and user experience.
Game Theory in Business and Marketing
In the business world, game theory provides valuable insights into competitive strategies, market dynamics, and consumer behavior. It helps companies develop effective marketing strategies, optimize pricing, and negotiate contracts.
Some business applications of game theory include:
- Competitive Strategies: Game theory helps businesses analyze competitors' strategies and develop effective counter-strategies.
- Pricing Optimization: Game theory models inform pricing decisions, considering the potential reactions of competitors and consumers.
- Contract Negotiation: Game theory analyzes negotiation scenarios, helping parties reach mutually beneficial agreements.
- Supply Chain Management: Game theory informs the optimization of supply chains, considering the strategic interactions between suppliers and buyers.
By applying game theory to business and marketing, companies can make more informed decisions and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Can Game Theory Predict Human Behavior?
Game theory offers valuable insights into human behavior by modeling strategic interactions and decision-making processes. While it provides a framework for understanding potential outcomes, predicting human behavior is inherently complex due to the diversity of individual preferences and motivations.
Some factors that influence the predictive power of game theory include:
- Rationality Assumption: Game theory assumes rational decision-making, which may not always align with real-world behavior.
- Incomplete Information: In many scenarios, players lack complete information about others' preferences and strategies.
- Psychological Factors: Human behavior is influenced by emotions, biases, and social dynamics, which can deviate from rational models.
While game theory provides a useful framework for analyzing strategic interactions, it is important to recognize its limitations and the complexity of human behavior.
Ethical Implications of Game Theory
Game theory raises important ethical considerations, particularly in scenarios involving competition, cooperation, and resource allocation. Understanding these implications is crucial for applying game theory responsibly in real-world situations.
Some ethical considerations include:
- Fairness and Equity: Game theory models should consider the fair distribution of resources and opportunities among players.
- Coercion and Manipulation: Game theory can be used to manipulate outcomes, raising ethical concerns about consent and autonomy.
- Social Impact: Game theory applications should consider their impact on society, including potential consequences for marginalized groups.
By addressing these ethical considerations, practitioners can ensure that game theory is applied in a manner that promotes fairness and social responsibility.
Common Misconceptions About Game Theory
Despite its widespread applications, game theory is often misunderstood or misrepresented. Addressing common misconceptions can help clarify its principles and enhance its effective use in various fields.
Some common misconceptions include:
- Game Theory is Only About Games: While game theory originated from analyzing games, its applications extend far beyond traditional board games and sports.
- Game Theory Guarantees Success: Game theory provides a framework for analyzing strategies, but it does not guarantee success in real-world scenarios.
- Game Theory Ignores Emotions: While game theory focuses on rational decision-making, it can incorporate psychological factors and emotions in more complex models.
By addressing these misconceptions, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of game theory and its practical applications.
What Are the Limitations of Game Theory?
While game theory provides valuable insights into strategic interactions, it has limitations that should be considered when applying its principles to real-world scenarios.
Some limitations of game theory include:
- Rationality Assumption: Game theory assumes rational decision-making, which may not always align with real-world behavior.
- Incomplete Information: In many scenarios, players lack complete information about others' preferences and strategies.
- Complexity of Human Behavior: Human behavior is influenced by emotions, biases, and social dynamics, which can deviate from rational models.
By acknowledging these limitations, practitioners can apply game theory more effectively and responsibly in various contexts.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of game theory?
Game theory aims to understand and analyze strategic interactions between decision-makers, providing insights into optimal strategies and potential outcomes.
2. How does game theory apply to everyday life?
Game theory applies to everyday life by helping individuals make informed decisions in competitive situations, such as negotiations, pricing, and resource allocation.
3. Can game theory be used to predict stock market behavior?
While game theory provides insights into strategic interactions, predicting stock market behavior is complex due to the influence of numerous factors and uncertainties.
4. How does game theory relate to artificial intelligence?
Game theory informs the development of AI systems that can navigate strategic interactions with humans and other AI agents, optimizing decision-making processes.
5. What is the difference between cooperative and non-cooperative games?
Cooperative games allow players to form alliances and work together, while non-cooperative games involve independent decision-making and competition.
6. How does game theory address ethical concerns?
Game theory addresses ethical concerns by considering fairness, equity, and social impact in strategic interactions, promoting responsible decision-making.
Conclusion
Game theory is a powerful framework for understanding strategic interactions and decision-making processes. Its applications span a wide range of fields, from economics and politics to biology and technology. By providing insights into competitive behavior and potential outcomes, game theory helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions and navigate complex environments effectively.
While game theory has its limitations, it remains an invaluable tool for analyzing strategic interactions and predicting potential outcomes. By understanding its principles and addressing ethical considerations, practitioners can apply game theory responsibly and effectively in real-world scenarios. As our understanding of strategic interactions continues to evolve, game theory will play an increasingly important role in shaping decision-making processes and informing strategies across various fields.
Article Recommendations

