Enhance Security With Multi-Factor Authentication: A Guide
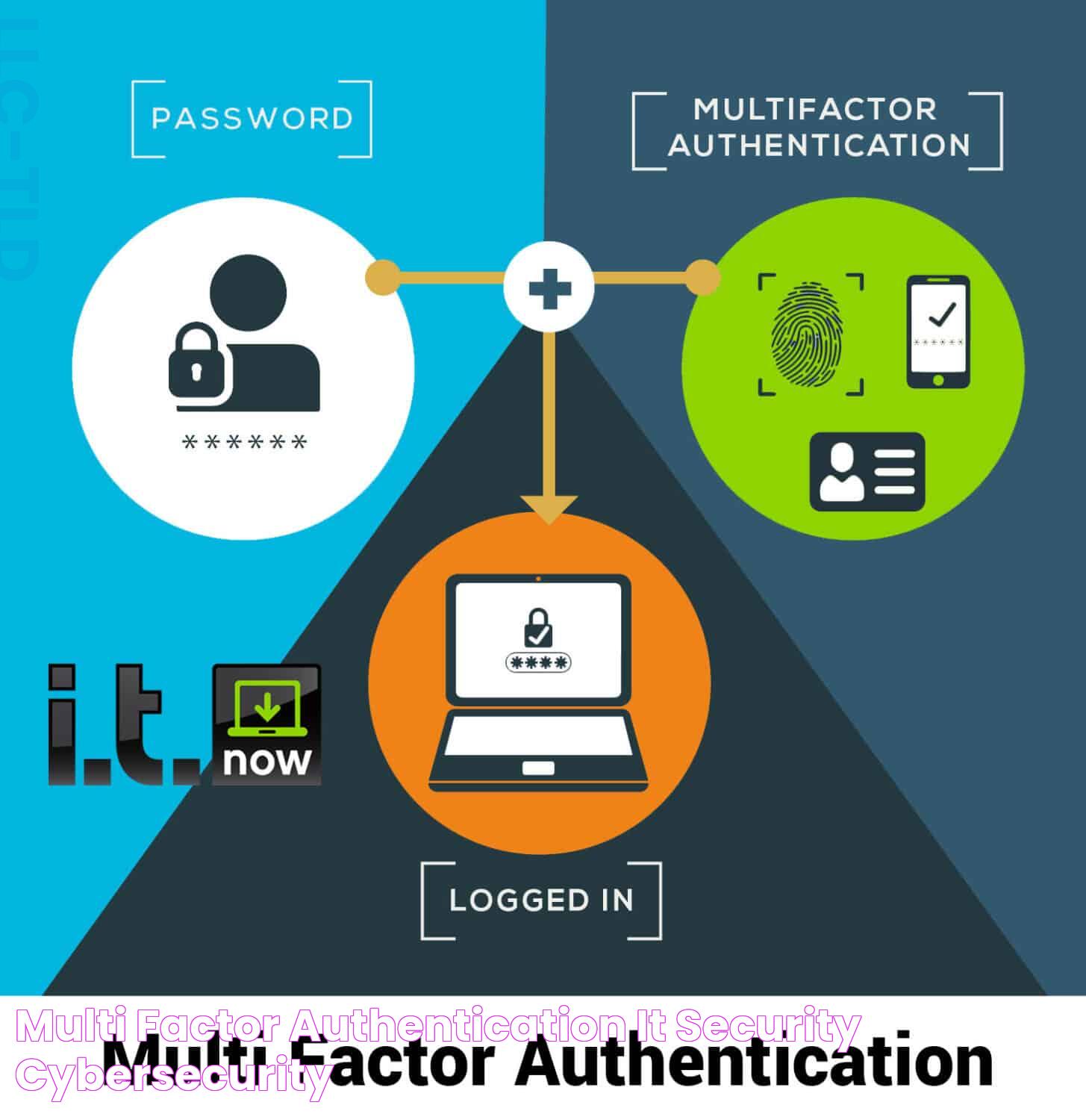
In an era where cyber threats loom large, safeguarding sensitive information has become paramount. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) stands as a robust solution to bolster security protocols, offering a multi-layered defense mechanism against unauthorized access. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, MFA ensures that even if one credential is compromised, additional layers of security remain intact.
Multi-factor authentication is not just a buzzword in the realm of cybersecurity; it's a necessity. As technology evolves, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. Traditional password systems are no longer sufficient to protect valuable data. Enter MFA, a system that combines something you know (a password), something you have (a smartphone or token), and something you are (biometric verification), making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to breach systems.
For businesses and individuals alike, implementing MFA is akin to adding an extra lock on the door to your digital assets. Not only does it provide peace of mind, but it also complies with regulatory standards and industry best practices. This article delves into the intricacies of multi-factor authentication, highlighting its importance, mechanisms, and implementation strategies to ensure your data remains secure in an increasingly digital world.
Read also:Innovative Screens The Role Of Tv In Modern Society
Table of Contents
- What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
- History of Authentication Methods
- How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
- Types of Authentication Factors
- Benefits of Using MFA
- Challenges in Implementing MFA
- How to Implement MFA in Your Organization?
- MFA in Different Industries
- MFA and Compliance Requirements
- Common Misconceptions About MFA
- Future of Multi-Factor Authentication
- MFA and User Experience
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user's identity. The goal of MFA is to create a layered defense that makes it more difficult for an unauthorized person to access a target such as a physical location, computing device, network, or database.
At its core, MFA combines two or more separate factors from different categories:
- Something you know: This could be a password, a PIN, or an answer to a security question.
- Something you have: This might be a smart card, a mobile device, or a hardware token.
- Something you are: This includes biometric verification such as fingerprints, retina scans, or voice recognition.
By requiring multiple forms of identity verification, MFA adds an additional layer of security beyond simple password protection. Even if one factor is compromised, unauthorized access is still prevented unless the other factors are also breached.
History of Authentication Methods
The journey of authentication methods has been transformative, evolving alongside technological advancements. Initially, authentication relied solely on simple passwords, a method that dates back to the early days of computing. However, as the digital landscape expanded, so did the vulnerabilities associated with single-factor authentication.
As cyber threats grew more sophisticated, the need for enhanced security measures became apparent. Two-factor authentication (2FA) emerged as a response, adding an extra layer by requiring a second form of verification. This method gained traction in the late 20th century, leveraging technologies such as smart cards and hardware tokens.
The rise of multi-factor authentication (MFA) marked a significant milestone in the evolution of security protocols. By integrating multiple verification factors, MFA offers a comprehensive approach to identity confirmation, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. As we continue to witness technological advancements, the future of authentication methods promises even more innovative solutions to safeguard our digital assets.
Read also:Essential Guide To College Football Games Everything You Need To Know
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) operates by requiring users to present two or more verification factors to gain access to a system, application, or device. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Initial Login Attempt: The user enters their username and password as the first factor of authentication.
- Additional Verification: Upon successful entry of the initial credentials, the system prompts the user for a second factor. This could be a one-time passcode (OTP) sent to a registered mobile device, a fingerprint scan, or a hardware token.
- Access Granted: Once the additional factor is verified, the user gains access to the desired resource. If any factor is incorrect or unavailable, access is denied.
This layered approach ensures that even if one factor is compromised, the system remains secure. MFA is adaptable, allowing organizations to choose factors based on their specific security needs and user convenience.
Types of Authentication Factors
Authentication factors are the building blocks of MFA, each providing a unique layer of security. These factors are generally categorized into three main types:
1. Knowledge Factors
These are something the user knows, such as:
- Passwords: The most common form of knowledge factor, requiring users to remember a secret word or phrase.
- PINs: Short numeric codes that are easy to remember and commonly used in combination with other factors.
- Security Questions: Answers to personal questions known only to the user.
2. Possession Factors
These are something the user has, including:
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices that generate time-sensitive passcodes.
- Smart Cards: Cards with embedded microchips that store authentication data.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones used to receive OTPs or run authentication apps.
3. Inherence Factors
These are something the user is, such as:
- Biometric Data: Fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns unique to the individual.
- Behavioral Biometrics: Patterns in user behavior, such as typing rhythm or mouse movement.
By leveraging a combination of these factors, MFA provides a comprehensive security solution that is both effective and user-friendly.
Benefits of Using MFA
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) offers numerous benefits that extend beyond enhanced security. Here are some key advantages of adopting MFA:
- Increased Security: By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries and regulatory bodies mandate the use of MFA to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
- Improved User Trust: Users feel more secure knowing that their data is protected by robust authentication methods.
- Reduced Fraud and Identity Theft: MFA minimizes the likelihood of identity theft and fraudulent activities by adding extra layers of protection.
- Adapts to Emerging Threats: MFA is continually evolving to address new cyber threats, ensuring ongoing security for users.
Overall, MFA provides a strong defense against cyber threats, making it an essential component of any robust security strategy.
Challenges in Implementing MFA
While multi-factor authentication (MFA) offers numerous benefits, its implementation can present certain challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for organizations to successfully deploy MFA solutions:
1. User Resistance
Users may perceive MFA as cumbersome or inconvenient, leading to resistance in adopting the new system. To address this, organizations must educate users about the importance of MFA and provide user-friendly solutions that minimize disruption.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
Implementing MFA can be complex, especially when integrating with legacy systems or applications. Organizations must ensure compatibility and seamless integration to avoid disruptions in operations.
3. Cost Considerations
MFA solutions may require significant investment in terms of software, hardware, and training. Organizations must weigh the cost against the potential security benefits to determine the most appropriate solution.
4. Managing Multiple Devices
With the proliferation of devices, managing authentication across various platforms can be challenging. Organizations must implement solutions that provide consistent and secure authentication across all devices.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of MFA far outweigh the difficulties, making it a worthwhile investment for organizations committed to enhancing their security posture.
How to Implement MFA in Your Organization?
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) in your organization requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to guide you through the process:
1. Assess Your Security Needs
Begin by evaluating your organization's security requirements, identifying critical assets, and determining the level of protection needed. Consider factors such as regulatory compliance, industry standards, and potential risks.
2. Choose the Right MFA Solution
Select an MFA solution that aligns with your organization's security needs and user convenience. Consider factors such as ease of integration, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
3. Educate and Train Users
Conduct training sessions to educate users about the importance of MFA and how it works. Provide clear instructions on how to use the new system and address any concerns or questions.
4. Integrate MFA with Existing Systems
Work with your IT team to integrate the chosen MFA solution with your existing systems and applications. Ensure compatibility and conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues.
5. Monitor and Optimize
Once MFA is implemented, continuously monitor its performance and gather user feedback. Use this information to make necessary adjustments and optimize the system for improved security and user experience.
By following these steps, your organization can successfully implement MFA and significantly enhance its security posture.
MFA in Different Industries
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is widely used across various industries to enhance security and protect sensitive data. Here are some examples of how MFA is applied in different sectors:
1. Financial Services
In the financial industry, MFA is crucial for protecting customer accounts and financial transactions. Banks and financial institutions use MFA to prevent fraud, identity theft, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
2. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use MFA to safeguard patient data and ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. MFA helps protect electronic health records (EHRs) and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive medical information.
3. Government
Government agencies implement MFA to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive data. MFA helps secure access to government systems and prevent cyberattacks on national assets.
4. Retail
Retail businesses use MFA to protect customer data and prevent unauthorized access to point-of-sale (POS) systems. MFA helps prevent data breaches and enhance customer trust.
By adopting MFA, organizations across different industries can strengthen their security measures and protect critical data from cyber threats.
MFA and Compliance Requirements
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) plays a vital role in meeting compliance requirements across various industries. Regulatory bodies often mandate the use of MFA to protect sensitive data and ensure secure access to systems. Here are some compliance standards that emphasize the importance of MFA:
1. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS requires organizations that handle cardholder data to implement MFA as part of their security measures. MFA is essential for securing access to cardholder data environments and preventing unauthorized access.
2. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA mandates the use of MFA to protect electronic health records (EHRs) and ensure patient data confidentiality. Healthcare organizations must implement MFA to comply with HIPAA's security requirements.
3. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR emphasizes the importance of data protection and privacy. Organizations that process personal data of EU citizens must implement MFA to secure access to sensitive information and comply with GDPR regulations.
4. Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
FISMA requires federal agencies to implement MFA as part of their security measures to protect government systems and data. MFA helps ensure secure access to federal systems and prevent cyber threats.
By implementing MFA, organizations can meet compliance requirements and demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive data.
Common Misconceptions About MFA
Despite its effectiveness, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions about MFA and the truths behind them:
1. MFA is Too Complicated
Many believe that MFA is complicated to set up and use. However, modern MFA solutions are designed to be user-friendly and easy to implement. Organizations can choose from a variety of options that best suit their needs and user preferences.
2. MFA is Only for Large Organizations
Some assume that MFA is only necessary for large organizations with significant resources. In reality, MFA is beneficial for organizations of all sizes, as it provides essential security against cyber threats.
3. MFA is Inconvenient for Users
While MFA adds an extra step to the authentication process, it significantly enhances security. Many MFA solutions offer seamless integrations and options such as biometric authentication, which are convenient for users.
4. MFA is Foolproof
Although MFA provides robust security, no system is entirely foolproof. It's important to combine MFA with other security measures and stay informed about emerging threats to maintain a strong security posture.
Understanding these misconceptions can help organizations make informed decisions about implementing MFA and enhancing their security strategies.
Future of Multi-Factor Authentication
As technology continues to evolve, so does the future of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Here are some trends and innovations that are shaping the future of MFA:
1. Biometrics and Behavioral Analytics
The use of biometrics and behavioral analytics is on the rise, providing more secure and convenient authentication methods. Technologies such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice recognition are becoming more prevalent in MFA solutions.
2. Passwordless Authentication
As the limitations of passwords become more apparent, passwordless authentication methods are gaining traction. These methods eliminate the need for passwords, relying on factors such as biometrics and possession for secure authentication.
3. AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being integrated into MFA solutions to enhance security and user experience. These technologies can analyze user behavior and detect anomalies, providing an additional layer of protection.
4. Decentralized Identity Solutions
Decentralized identity solutions are emerging as a way to enhance privacy and security. By allowing users to control their identity data, these solutions provide more secure and user-centric authentication methods.
The future of MFA promises innovative solutions that will continue to enhance security and protect against cyber threats.
MFA and User Experience
While multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security, it's important to balance security with user experience. Here are some strategies to ensure a positive user experience when implementing MFA:
1. Choose User-Friendly Solutions
Select MFA solutions that are intuitive and easy to use. Consider options such as biometric authentication, which offer a seamless and convenient experience for users.
2. Provide Clear Instructions
Offer clear instructions and support to help users understand how to use MFA. Provide resources such as tutorials and FAQs to address common questions and concerns.
3. Offer Flexibility and Choice
Allow users to choose from multiple authentication methods based on their preferences and needs. Providing flexibility can enhance user satisfaction and encourage adoption.
4. Monitor and Gather Feedback
Continuously monitor user feedback and make adjustments to improve the MFA experience. Use feedback to identify areas for improvement and optimize the system for user convenience.
By prioritizing user experience, organizations can ensure that MFA enhances security without compromising usability.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary purpose of multi-factor authentication?
The primary purpose of multi-factor authentication (MFA) is to provide an additional layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access systems or data.
2. Can MFA be used in conjunction with single sign-on (SSO) solutions?
Yes, MFA can be integrated with single sign-on (SSO) solutions to enhance security. By combining MFA with SSO, organizations can streamline the authentication process while maintaining robust security measures.
3. How does MFA improve data protection and prevent breaches?
MFA improves data protection by requiring multiple authentication factors, which reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if one factor is compromised. This layered approach makes it more difficult for cybercriminals to breach systems and access sensitive data.
4. What are some common authentication methods used in MFA?
Common authentication methods used in MFA include passwords, security questions, hardware tokens, smart cards, mobile devices, and biometric verification such as fingerprints and facial recognition.
5. Is MFA suitable for small businesses?
Yes, MFA is suitable for businesses of all sizes, including small businesses. By implementing MFA, small businesses can protect sensitive data and reduce the risk of cyber threats, enhancing their overall security posture.
6. How does MFA help with regulatory compliance?
MFA helps with regulatory compliance by meeting security requirements mandated by various industry standards and regulations. Implementing MFA demonstrates an organization's commitment to data protection and compliance with regulations such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a powerful security tool that enhances the protection of sensitive data and systems. By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA provides a robust defense against unauthorized access and cyber threats. As technology continues to evolve, MFA will play an increasingly important role in safeguarding digital assets and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
While implementing MFA may present certain challenges, the benefits far outweigh the difficulties. Organizations across various industries can leverage MFA to strengthen their security posture, build user trust, and protect against emerging threats. By prioritizing user experience and staying informed about the latest trends and innovations, organizations can successfully implement MFA and ensure a secure digital environment.
For more information on multi-factor authentication and security best practices, visit NIST.
Article Recommendations

