Waardenburg Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, And Management
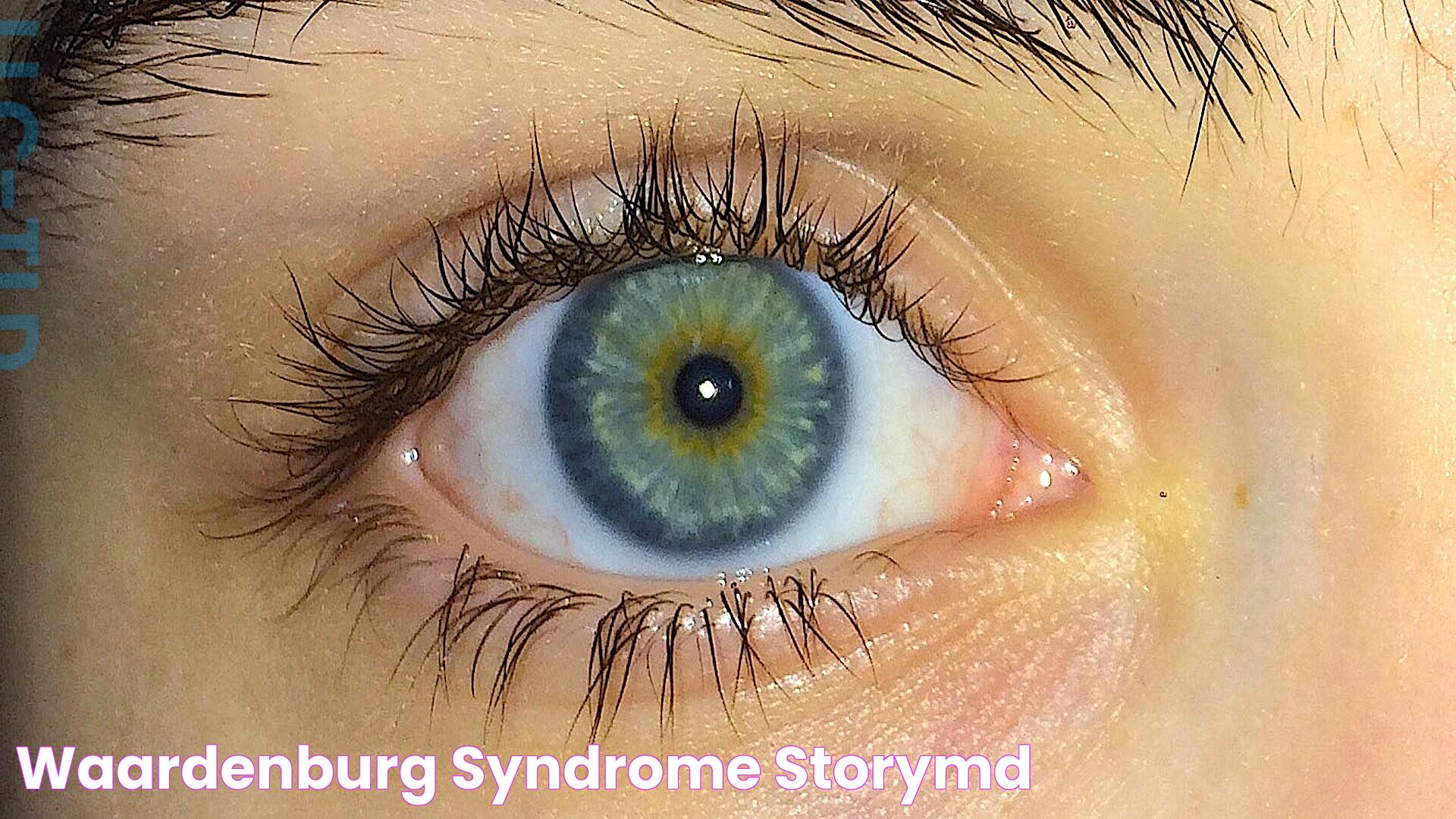
Waardenburg Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the pigmentation of the hair, skin, and eyes, and can also cause hearing loss. Named after Dutch ophthalmologist Petrus Johannes Waardenburg, who first identified the syndrome in 1951, it is known for its distinctive features such as differently colored eyes and a white forelock of hair. Despite its rarity, Waardenburg Syndrome has gained attention due to its striking characteristics and the challenges it presents in terms of diagnosis and management.
This genetic condition is caused by mutations in several genes that are involved in the development of neural crest cells, which are essential for the formation of various tissues and organs. Although Waardenburg Syndrome is classified into four major types, each with its own set of symptoms and genetic causes, individuals with this syndrome may experience varying degrees of hearing loss and changes in pigmentation. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
With advancements in genetic research and a growing understanding of the molecular basis of Waardenburg Syndrome, there are now more opportunities for early detection and intervention. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of Waardenburg Syndrome, providing a comprehensive overview for those affected by the condition, healthcare professionals, and the general public. By raising awareness and promoting research, we can improve the quality of life for individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome and their families.
Read also:Patricia Arkette The Multifaceted Persona And Her Unforgettable Impact
Table of Contents
- What is Waardenburg Syndrome?
- Genetic Causes of Waardenburg Syndrome
- Types of Waardenburg Syndrome
- Common Symptoms of Waardenburg Syndrome
- How is Waardenburg Syndrome Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Waardenburg Syndrome
- Living with Waardenburg Syndrome
- Can Waardenburg Syndrome Be Prevented?
- Waardenburg Syndrome and Hearing Loss
- Impact of Waardenburg Syndrome on Quality of Life
- Support and Resources for Waardenburg Syndrome
- Recent Research on Waardenburg Syndrome
- Waardenburg Syndrome in Pop Culture
- Frequently Asked Questions about Waardenburg Syndrome
- Conclusion
What is Waardenburg Syndrome?
Waardenburg Syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by a combination of hearing loss and pigmentation anomalies. It is an autosomal dominant condition, meaning a single copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. The syndrome is highly variable, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. The condition's hallmark features include dystopia canthorum (lateral displacement of the inner canthi of the eyes), heterochromia iridum (differently colored eyes), and a white forelock of hair. These distinct features often make Waardenburg Syndrome recognizable even at birth.
Genetic Causes of Waardenburg Syndrome
The genetic basis of Waardenburg Syndrome lies in mutations in several genes responsible for the development and function of neural crest cells. These include PAX3, MITF, SOX10, EDNRB, and EDN3, among others. Each gene mutation corresponds to different types of the syndrome, contributing to its diverse presentation. PAX3 mutations, for example, are primarily associated with Waardenburg Syndrome types 1 and 3, while MITF mutations are linked to type 2. Understanding the genetic underpinnings helps in precise diagnosis and genetic counseling.
Types of Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg Syndrome is classified into four types, each with distinct genetic causes and clinical features:
- Type 1: Characterized by dystopia canthorum, hearing loss, and pigmentation changes. It is often associated with PAX3 gene mutations.
- Type 2: Similar to Type 1 but without dystopia canthorum. It is frequently linked to MITF gene mutations.
- Type 3 (Klein-Waardenburg syndrome): Includes musculoskeletal abnormalities in addition to the features of Type 1. It is also associated with PAX3 mutations.
- Type 4 (Waardenburg-Shah syndrome): Combines features of Waardenburg Syndrome with Hirschsprung disease, a condition affecting the colon. This type is related to mutations in the EDNRB, EDN3, or SOX10 genes.
Common Symptoms of Waardenburg Syndrome
Symptoms of Waardenburg Syndrome can vary widely but typically include:
- Hearing loss, which can be unilateral or bilateral and ranges from mild to profound.
- Distinctive pigmentation patterns, such as heterochromia iridum, white forelock, and patchy skin depigmentation.
- Facial features such as a broad nasal root and dystopia canthorum.
- In some cases, intestinal issues related to Hirschsprung disease (particularly in Type 4).
These symptoms are not only diagnostically significant but also impact the daily lives of those affected.
How is Waardenburg Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Waardenburg Syndrome is primarily clinical, based on the presence of characteristic features such as dystopia canthorum, hearing loss, and pigmentation anomalies. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying specific gene mutations associated with the syndrome. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing hearing loss and other associated conditions effectively. Healthcare providers may use a combination of physical examinations, audiological tests, and genetic counseling to arrive at a comprehensive diagnosis.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Foreigner Songs Timeless Hits And Their Impact
Treatment Options for Waardenburg Syndrome
There is currently no cure for Waardenburg Syndrome, but various treatment options are available to manage its symptoms:
- Hearing aids and cochlear implants to address hearing loss.
- Speech therapy to support communication development.
- Surgical interventions for associated conditions, such as Hirschsprung disease.
- Regular monitoring and supportive care for any developmental or educational needs.
Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach are key to improving outcomes for individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome.
Living with Waardenburg Syndrome
Living with Waardenburg Syndrome can pose challenges, particularly concerning hearing loss and social interactions due to distinct physical features. However, with the right support and resources, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Families and caregivers play a crucial role in providing emotional and practical support, helping those affected to navigate daily life and access necessary services. Community support groups and advocacy organizations can also offer valuable resources and connections.
Can Waardenburg Syndrome Be Prevented?
Currently, there is no way to prevent Waardenburg Syndrome, as it is a genetic condition. However, genetic counseling can provide valuable information for families with a history of the syndrome. Prospective parents can undergo genetic testing to assess the risk of passing the condition to their offspring. By understanding the genetic implications, families can make informed decisions and prepare for any potential challenges.
Waardenburg Syndrome and Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is one of the most significant challenges associated with Waardenburg Syndrome, affecting communication and social development. The severity of hearing loss varies among individuals, and early detection is crucial for implementing effective interventions. Audiological evaluations and appropriate hearing devices can significantly improve hearing and quality of life. Ongoing research aims to develop advanced therapies to address hearing loss at the genetic level.
Impact of Waardenburg Syndrome on Quality of Life
The quality of life for individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome can be influenced by several factors, including the severity of symptoms, access to medical care, and social support. While the condition poses challenges, many individuals lead successful and satisfying lives. Advances in medical care and public awareness can help reduce stigma and improve the overall well-being of those affected. Encouraging inclusivity and understanding within communities is essential for fostering a supportive environment.
Support and Resources for Waardenburg Syndrome
Various organizations and support groups provide resources and assistance for individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome and their families. These include:
- The Waardenburg Syndrome Foundation
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD)
- Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD)
- Deaf and hard of hearing advocacy groups
These resources offer information, support networks, and advocacy services, helping individuals navigate the challenges associated with Waardenburg Syndrome and connect with others facing similar experiences.
Recent Research on Waardenburg Syndrome
Research on Waardenburg Syndrome continues to advance, focusing on genetic discoveries and potential treatments. Studies aim to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the condition and explore innovative therapies. Gene therapy and regenerative medicine are promising areas of research that could offer new solutions for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups are essential for driving progress and ensuring that research translates into tangible benefits for those affected.
Waardenburg Syndrome in Pop Culture
Waardenburg Syndrome has occasionally been depicted in popular culture, often highlighting its distinctive physical features. However, accurate and sensitive portrayals are important to raise awareness and promote understanding. By showcasing the experiences of individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome, media can play a role in challenging stereotypes and fostering empathy. Positive representation can contribute to reducing stigma and promoting inclusivity for people with the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions about Waardenburg Syndrome
1. What causes Waardenburg Syndrome?
Waardenburg Syndrome is caused by mutations in specific genes responsible for neural crest cell development, such as PAX3, MITF, SOX10, EDNRB, and EDN3.
2. How common is Waardenburg Syndrome?
Waardenburg Syndrome is a rare condition, affecting approximately 1 in 40,000 people worldwide.
3. Can Waardenburg Syndrome be inherited?
Yes, Waardenburg Syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition, meaning it can be inherited from an affected parent. However, new mutations can also occur spontaneously.
4. Is there a cure for Waardenburg Syndrome?
There is no cure for Waardenburg Syndrome, but treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
5. How is Waardenburg Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on clinical features and can be confirmed through genetic testing to identify specific gene mutations.
6. What support is available for families affected by Waardenburg Syndrome?
Support groups, advocacy organizations, and healthcare providers offer resources and assistance for families, providing information, networks, and guidance on managing the condition.
Conclusion
Waardenburg Syndrome, although rare, presents unique challenges and opportunities for those affected. With a deeper understanding of its genetic foundations and continued advancements in medical research, individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome can look forward to improved management options and support systems. Awareness and inclusivity are key to fostering a supportive environment, allowing people with Waardenburg Syndrome to lead fulfilling lives and contribute to their communities. By embracing diversity and promoting understanding, society can help reduce the stigma associated with this and other genetic conditions.
Article Recommendations

