Mastering The Art Of The Dependent Variable: A Step-by-Step Guide
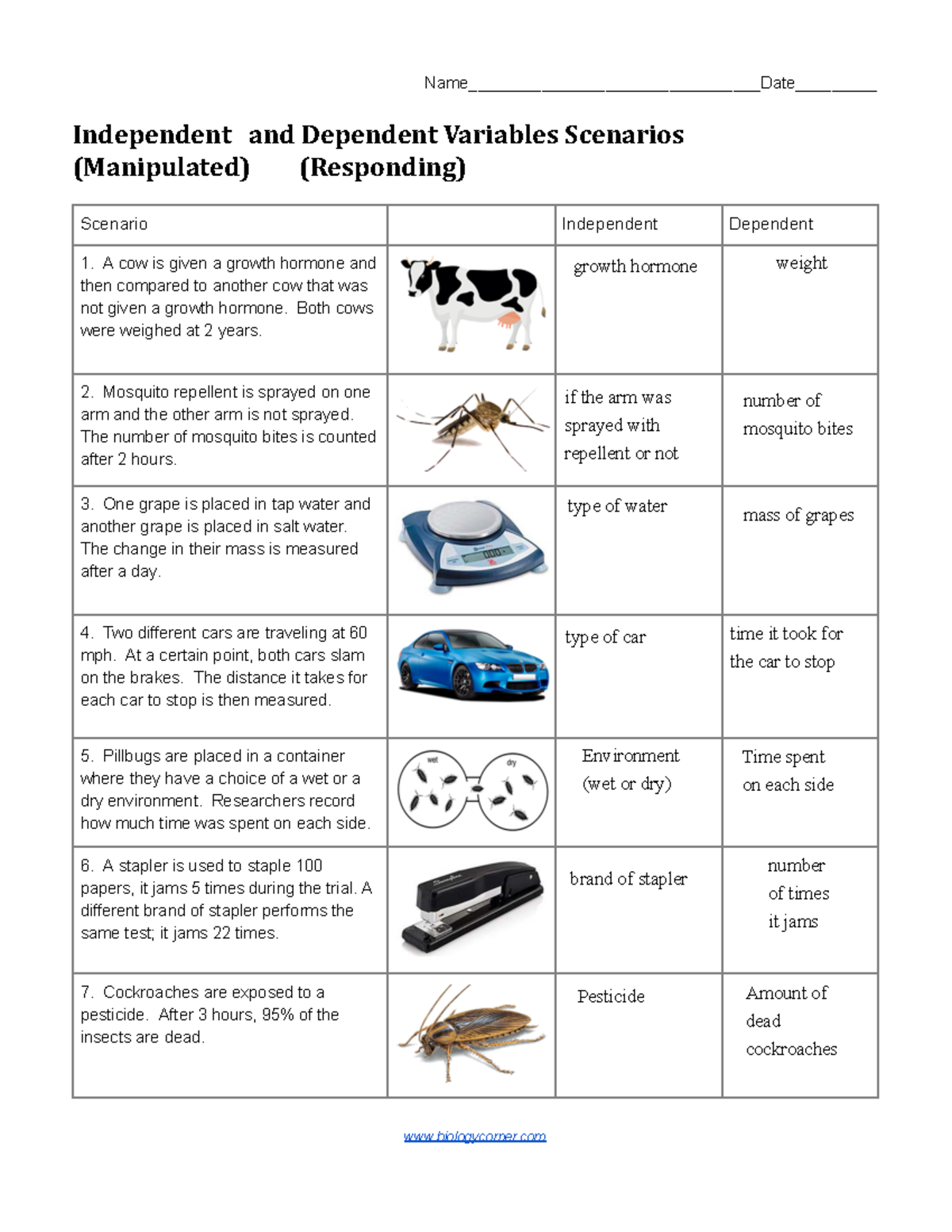
The concept of a "dependent variable" is integral to the world of research and experimentation. It is the variable that researchers measure or observe to determine the effect of different manipulations or conditions. Understanding how to identify and analyze the dependent variable is crucial for drawing accurate conclusions and building a solid foundation for scientific inquiry. This guide will delve into the nuances of dependent variables, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in various fields of study.
Dependent variables play a pivotal role in hypothesis testing and experimental design. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can assess the impact of independent variables and evaluate causal relationships. This process aids in refining theories and developing a deeper understanding of complex phenomena. As we navigate through this guide, we will explore the importance of dependent variables in research, how to identify them, and the challenges that come with their measurement.
In the realm of data analysis, dependent variables are vital for statistical modeling and hypothesis testing. They enable researchers to quantify the effects of different factors on outcomes of interest. This guide will provide insights into the methods and techniques used to measure and analyze dependent variables, ensuring you have a well-rounded understanding of their significance in scientific investigations. Join us as we uncover the intricacies of dependent variables and their indispensable role in the pursuit of knowledge.
Read also:Aaron Gordon Stats A Deep Dive Into His Career Achievements
Table of Contents
- What is a Dependent Variable?
- Importance of Dependent Variables in Research
- How to Identify Dependent Variables?
- Dependent Variable vs. Independent Variable
- Examples of Dependent Variables Across Different Fields
- Challenges in Measuring Dependent Variables
- Statistical Analysis of Dependent Variables
- Role of Dependent Variables in Experimental Design
- How Do Dependent Variables Affect Results?
- Dependent Variables in Social Sciences
- Dependent Variables in Natural Sciences
- Dependent Variable in Statistical Modeling
- Common Misconceptions About Dependent Variables
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a Dependent Variable?
The dependent variable is a fundamental concept in the realm of scientific research and experimentation. It is the variable that researchers aim to measure or observe to determine the effect of changes in other variables, known as independent variables. Essentially, the dependent variable is the outcome that is influenced by the manipulations or interventions applied during an experiment. Understanding the dependent variable is crucial for analyzing the causal relationships between variables and drawing meaningful conclusions.
In any given study, the dependent variable is the factor that is expected to change or respond as a result of alterations in the independent variable. For instance, in a clinical trial assessing the effectiveness of a new drug, the dependent variable may be the patient's health outcome, such as blood pressure or cholesterol levels. Researchers manipulate the independent variable (the drug) and observe the effects on the dependent variable (health outcome) to determine the drug's efficacy.
The identification and measurement of the dependent variable are pivotal steps in the research process. It requires careful consideration of the research question and the theoretical framework guiding the study. By clearly defining the dependent variable, researchers can ensure that their findings are reliable, valid, and applicable to real-world scenarios. The dependent variable serves as a bridge between theory and practice, allowing researchers to test hypotheses and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
Importance of Dependent Variables in Research
Dependent variables hold significant importance in the research process, serving as the cornerstone for hypothesis testing and experimental design. Their primary role is to provide measurable evidence of the impact of independent variables, allowing researchers to assess causal relationships and draw meaningful conclusions. Understanding the importance of dependent variables is essential for conducting rigorous and valid research.
One of the key reasons dependent variables are vital in research is their ability to quantify the effects of different conditions or interventions. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can determine the extent to which the independent variable influences the outcome. This quantification is crucial for comparing results across studies, replicating findings, and building a solid evidence base for theoretical frameworks.
Moreover, dependent variables play a critical role in refining and testing hypotheses. They provide the data needed to evaluate whether the proposed relationships between variables hold true. By examining the changes in the dependent variable, researchers can either support or refute their hypotheses, contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge. The dependent variable serves as the link between theoretical propositions and empirical evidence, facilitating the development of robust and reliable scientific theories.
Read also:Remarkable History And Influence Of Diane Wildenstein
How to Identify Dependent Variables?
Identifying the dependent variable is a crucial step in the research process, as it determines the focus of the study and guides the measurement and analysis of data. The dependent variable is the outcome that researchers aim to observe or measure in response to changes in the independent variable. To accurately identify the dependent variable, researchers must carefully consider the research question, the theoretical framework, and the nature of the study.
One effective approach to identifying the dependent variable is to clearly articulate the research question or hypothesis. By defining the specific outcome that the study aims to investigate, researchers can pinpoint the dependent variable. For instance, in a study examining the impact of exercise on weight loss, the dependent variable would be weight loss, as it is the outcome being measured in response to the independent variable (exercise).
Additionally, researchers should consider the theoretical framework guiding the study. The dependent variable should align with the theoretical propositions and constructs being tested. It is essential to ensure that the dependent variable is measurable and quantifiable, allowing for accurate data collection and analysis. By considering these factors, researchers can effectively identify the dependent variable and design a study that yields meaningful and valid results.
Dependent Variable vs. Independent Variable
In the realm of scientific research, it is essential to distinguish between dependent and independent variables, as they play distinct roles in the research process. Understanding the difference between these variables is crucial for designing experiments, analyzing data, and drawing valid conclusions. Let's delve into the key distinctions between dependent and independent variables and their significance in research.
The independent variable is the factor that researchers manipulate or control to investigate its effect on the dependent variable. It is the variable that is deliberately altered or varied to observe the resulting changes in the dependent variable. In contrast, the dependent variable is the outcome that is measured or observed in response to changes in the independent variable. It is the variable that researchers aim to explain or predict based on the influence of the independent variable.
In an experimental study, the independent variable is often referred to as the "cause," while the dependent variable is considered the "effect." For example, in a study examining the impact of different teaching methods on student performance, the teaching methods would be the independent variable, and student performance would be the dependent variable. By manipulating the independent variable (teaching methods), researchers aim to observe changes in the dependent variable (student performance).
Examples of Dependent Variables Across Different Fields
Dependent variables are utilized in various fields of study, each with its unique context and application. By examining examples of dependent variables across different disciplines, we can gain a deeper understanding of their significance and role in research. Let's explore some examples of dependent variables in diverse fields and how they contribute to scientific inquiry.
In the field of psychology, dependent variables are often used to measure behavioral outcomes or psychological responses. For instance, in a study investigating the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance, the dependent variable may be the participants' reaction times or accuracy on cognitive tasks. By assessing changes in the dependent variable, researchers can evaluate the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive functioning.
In the realm of medicine, dependent variables are frequently used to assess health outcomes or treatment efficacy. For example, in a clinical trial evaluating a new medication for hypertension, the dependent variable may be the patients' blood pressure levels. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can determine the effectiveness of the medication in lowering blood pressure and improving cardiovascular health.
Challenges in Measuring Dependent Variables
Measuring dependent variables can present several challenges in the research process, impacting the accuracy and validity of findings. These challenges arise from various factors, including measurement errors, confounding variables, and issues related to the operationalization of the dependent variable. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for conducting rigorous and reliable research.
One common challenge in measuring dependent variables is the presence of measurement errors. These errors can arise from inaccuracies in data collection instruments, human error, or variability in the measurement process. To mitigate measurement errors, researchers must ensure that their data collection instruments are reliable, valid, and calibrated appropriately. Additionally, employing standardized measurement protocols and conducting pilot tests can help identify and address potential measurement errors.
Another challenge in measuring dependent variables is the influence of confounding variables. Confounding variables are extraneous factors that can impact the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, leading to biased or misleading results. To address this challenge, researchers can use techniques such as randomization, control groups, or statistical adjustments to account for the effects of confounding variables and isolate the true relationship between the variables of interest.
Statistical Analysis of Dependent Variables
Statistical analysis plays a crucial role in the interpretation and understanding of dependent variables in research. By employing statistical techniques, researchers can analyze the data collected, identify patterns, and draw meaningful conclusions about the relationships between variables. Let's explore some common statistical methods used to analyze dependent variables and their significance in research.
One of the most widely used statistical methods for analyzing dependent variables is regression analysis. Regression analysis allows researchers to examine the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. By fitting a regression model to the data, researchers can assess the strength and direction of the relationship, identify significant predictors, and make predictions about the dependent variable based on the values of the independent variables.
Another commonly used statistical technique for analyzing dependent variables is analysis of variance (ANOVA). ANOVA is used to compare the means of the dependent variable across different groups or conditions. By conducting an ANOVA, researchers can determine whether there are significant differences in the dependent variable between the groups, allowing for the evaluation of the effects of different interventions or treatments.
Role of Dependent Variables in Experimental Design
Dependent variables play a crucial role in experimental design, serving as the focal point for data collection and analysis. Experimental design is a systematic approach used to investigate the relationships between variables and test hypotheses. Understanding the role of dependent variables in experimental design is essential for designing robust and valid experiments that yield meaningful and reliable results.
In experimental design, the dependent variable is the outcome that researchers aim to measure or observe in response to changes in the independent variable. It is the variable that provides the data needed to evaluate the effects of different conditions or interventions. The dependent variable is carefully selected and defined to align with the research question and the theoretical framework guiding the study.
Moreover, the dependent variable serves as the basis for hypothesis testing in experimental design. Researchers formulate hypotheses about the expected relationship between the independent and dependent variables and design experiments to test these hypotheses. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can determine whether the hypotheses are supported or refuted, contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
How Do Dependent Variables Affect Results?
Dependent variables have a significant impact on the results of research studies, as they provide the data needed to evaluate the effects of different conditions or interventions. Understanding how dependent variables affect results is essential for interpreting findings and drawing valid conclusions. Let's explore the ways in which dependent variables can influence the outcomes of research studies.
One of the key ways in which dependent variables affect results is through their measurement and operationalization. The accuracy and precision of the measurement of the dependent variable can significantly impact the validity and reliability of the findings. If the dependent variable is not accurately measured, the results may be biased or misleading, leading to incorrect conclusions about the relationships between variables.
Additionally, the choice of the dependent variable can influence the interpretation of the results. The dependent variable should align with the research question and the theoretical framework guiding the study. If the dependent variable is not appropriately selected or defined, the findings may not accurately reflect the intended outcomes of the study, limiting the generalizability and applicability of the results.
Dependent Variables in Social Sciences
In the field of social sciences, dependent variables are used to measure a wide range of outcomes, including behavioral, psychological, and social phenomena. Understanding the role of dependent variables in social sciences is essential for designing studies that yield meaningful and valid results. Let's explore some examples of dependent variables in social sciences and their significance in research.
In psychology, dependent variables are often used to measure behavioral outcomes or psychological responses. For instance, in a study examining the effects of stress on cognitive performance, the dependent variable may be the participants' reaction times or accuracy on cognitive tasks. By assessing changes in the dependent variable, researchers can evaluate the impact of stress on cognitive functioning and draw meaningful conclusions.
In sociology, dependent variables are used to measure social phenomena and outcomes. For example, in a study investigating the effects of socioeconomic status on educational attainment, the dependent variable may be the participants' educational attainment levels. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can evaluate the impact of socioeconomic status on educational outcomes and contribute to the understanding of social inequality.
Dependent Variables in Natural Sciences
In the field of natural sciences, dependent variables are used to measure a wide range of outcomes, including physical, chemical, and biological phenomena. Understanding the role of dependent variables in natural sciences is essential for designing experiments that yield meaningful and valid results. Let's explore some examples of dependent variables in natural sciences and their significance in research.
In biology, dependent variables are often used to measure physiological or biological outcomes. For instance, in a study investigating the effects of a new drug on cell growth, the dependent variable may be the rate of cell growth. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can evaluate the impact of the drug on cell growth and contribute to the understanding of biological processes.
In chemistry, dependent variables are used to measure chemical reactions and outcomes. For example, in a study examining the effects of temperature on reaction rates, the dependent variable may be the reaction rate. By measuring changes in the dependent variable, researchers can evaluate the impact of temperature on reaction rates and contribute to the understanding of chemical processes.
Dependent Variable in Statistical Modeling
In statistical modeling, the dependent variable is the outcome that researchers aim to predict or explain based on the values of one or more independent variables. Understanding the role of the dependent variable in statistical modeling is essential for developing accurate and reliable models that yield meaningful and valid results. Let's explore the significance of the dependent variable in statistical modeling and its role in data analysis.
In statistical modeling, the dependent variable is the focus of the analysis, as it is the outcome that researchers aim to predict or explain. The dependent variable is carefully selected and defined to align with the research question and the theoretical framework guiding the study. By accurately measuring and analyzing the dependent variable, researchers can develop models that provide insights into the relationships between variables and contribute to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Moreover, the dependent variable plays a crucial role in model evaluation and validation. Researchers assess the accuracy and reliability of their models by comparing the predicted values of the dependent variable with the observed values. By evaluating the model's performance, researchers can refine their models, improve their predictive accuracy, and enhance their understanding of the relationships between variables.
Common Misconceptions About Dependent Variables
Despite their importance in research, there are several common misconceptions about dependent variables that can impact the validity and reliability of findings. Understanding and addressing these misconceptions is essential for conducting rigorous and reliable research. Let's explore some common misconceptions about dependent variables and their implications for research.
One common misconception about dependent variables is that they are always directly measurable. In reality, dependent variables may be complex constructs that require careful operationalization and measurement. Researchers must ensure that their measurement instruments are reliable and valid, allowing for accurate data collection and analysis.
Another misconception is that the dependent variable is always the "effect" in a cause-and-effect relationship. While the dependent variable is often referred to as the "effect," this is not always the case. In some studies, the dependent variable may be an outcome that is influenced by multiple factors, and researchers must consider the potential influence of confounding variables and other factors that may impact the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main purpose of a dependent variable?
The main purpose of a dependent variable is to measure the effect of changes in the independent variable. It serves as the outcome that researchers aim to observe or measure in response to manipulations or interventions, allowing for the evaluation of causal relationships between variables.
How do you determine the dependent variable in a study?
To determine the dependent variable in a study, researchers must clearly define the research question or hypothesis, consider the theoretical framework guiding the study, and ensure that the dependent variable is measurable and quantifiable. The dependent variable should align with the intended outcomes of the study and provide meaningful data for analysis.
Can there be more than one dependent variable in a study?
Yes, a study can have multiple dependent variables, especially when researchers aim to investigate different outcomes or aspects of a phenomenon. In such cases, researchers must ensure that each dependent variable is clearly defined, measurable, and relevant to the research question.
What is the difference between a dependent variable and a response variable?
The terms "dependent variable" and "response variable" are often used interchangeably in research. Both refer to the outcome that researchers measure or observe in response to changes in the independent variable. However, "response variable" is more commonly used in the context of statistical analysis and modeling.
How can confounding variables affect the measurement of dependent variables?
Confounding variables can impact the measurement of dependent variables by introducing bias or variability in the results. They can obscure the true relationship between the independent and dependent variables, leading to inaccurate or misleading conclusions. Researchers must account for confounding variables through techniques such as randomization, control groups, or statistical adjustments.
Why is it important to operationalize dependent variables?
Operationalizing dependent variables is crucial for ensuring that they are measurable and quantifiable. By clearly defining how the dependent variable will be measured, researchers can ensure consistency and accuracy in data collection and analysis, contributing to the validity and reliability of the findings.
Conclusion
The concept of the dependent variable is fundamental to the research process, serving as the cornerstone for hypothesis testing, experimental design, and data analysis. Understanding the role and significance of dependent variables is essential for conducting rigorous and valid research that contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge. By accurately identifying, measuring, and analyzing dependent variables, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions about the relationships between variables and build a solid evidence base for theoretical frameworks.
This guide has explored the intricacies of dependent variables, providing insights into their importance in research, how to identify and measure them, and the challenges associated with their analysis. By mastering the art of the dependent variable, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their findings, contributing to the development of robust and reliable scientific theories. As we continue to explore the complexities of dependent variables, let us strive to advance our understanding of the world and contribute to the pursuit of knowledge.
Article Recommendations

